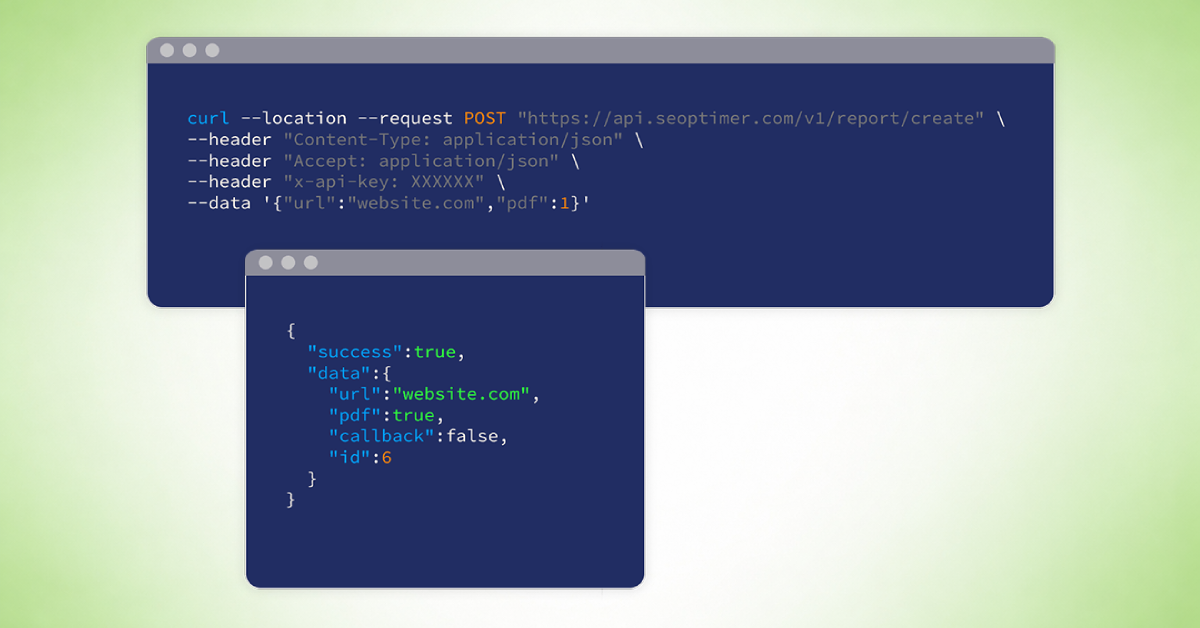
An SEO crawl is the process of scanning a website by analyzing each page for technical and on-page SEO issues. This helps identify problems that may affect search engine visibility, indexing, site structure, and overall site health.
In this guide, we highlight some of the most common issues detected by SEOptimer’s SEO Crawler.
These insights are based on data from real crawls performed by SEOptimer users across a wide range of websites and industries.
Let’s take a closer look at the most common site issues our SEO Crawler finds.
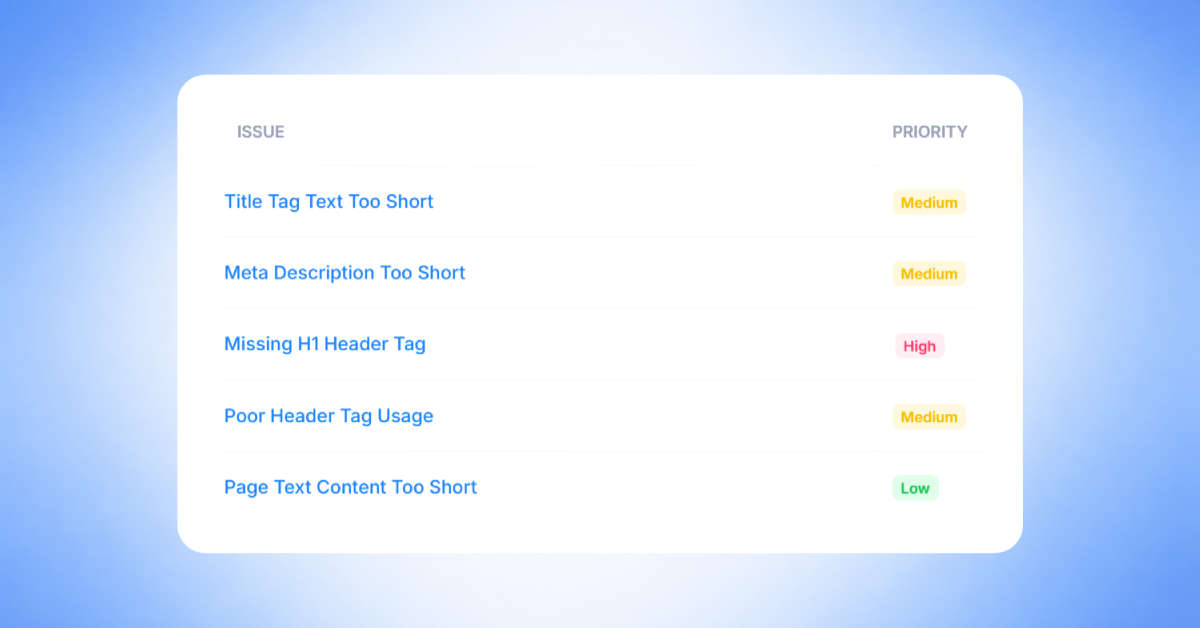
Top 10 Most Common Site Issues
1. Title Tag Text Too Short
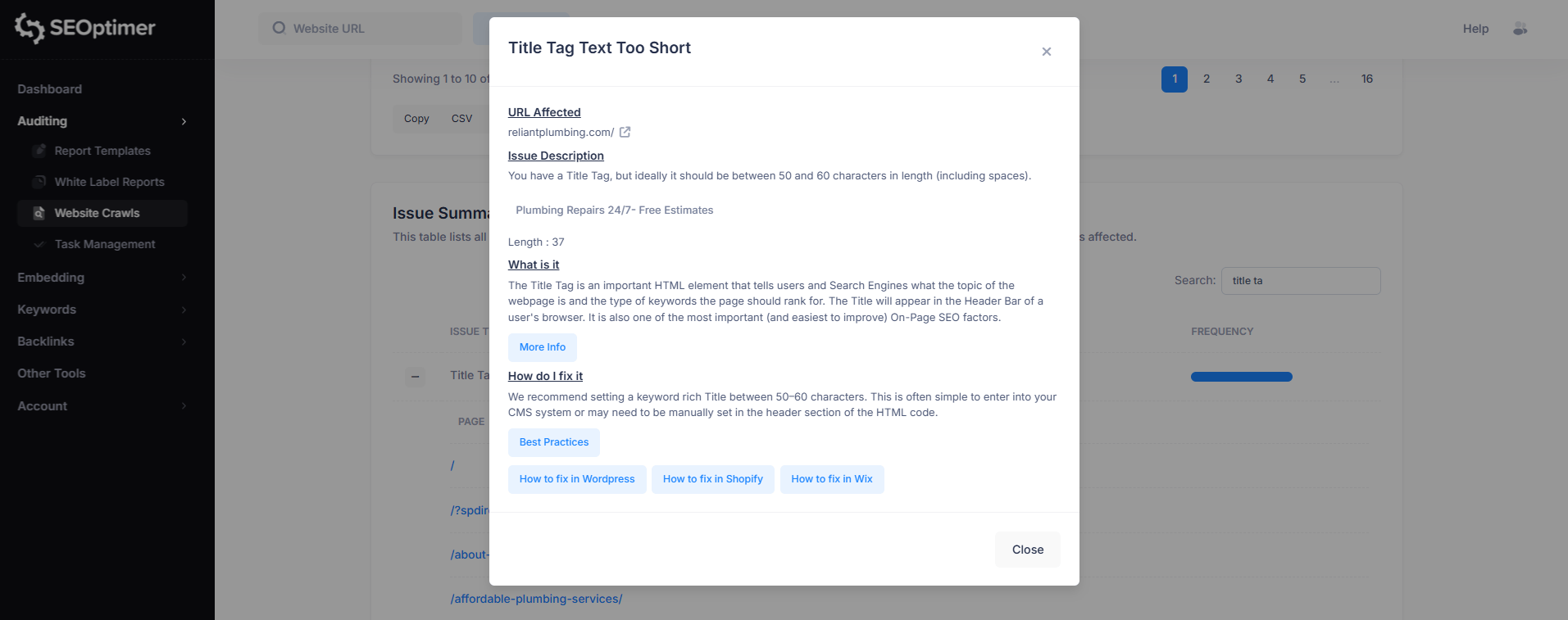
Priority: Medium
This issue means the page’s title tag is shorter than the recommended length (typically 50–60 characters, including spaces).
While short titles aren’t always harmful, they can reduce your ability to clearly describe the page and include important keywords.
To fix this, update the page title to be more descriptive and keyword-focused while keeping it within the recommended character range.
This can usually be done in your CMS SEO settings or directly in the page’s HTML.
Additional Reading:
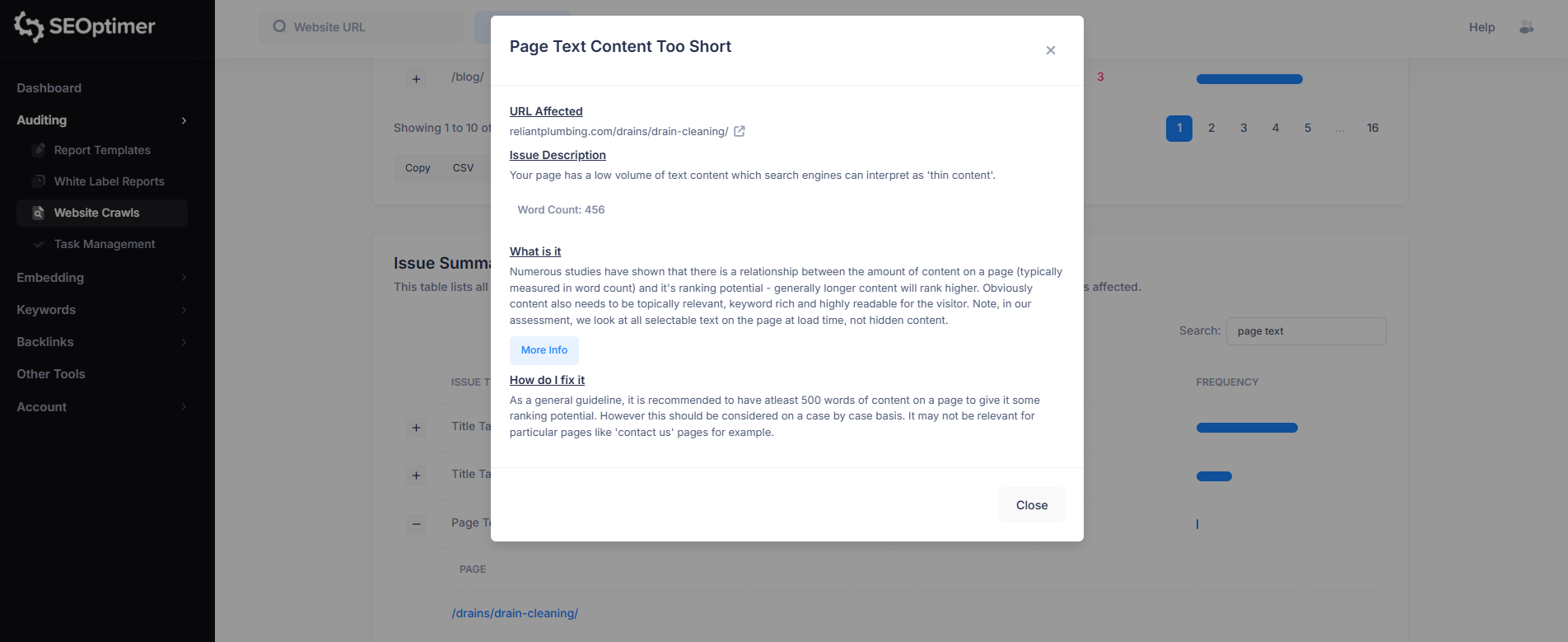
2. Page Text Content Too Short
Priority: Low
This issue means the page contains very little visible text content, which may be seen by search engines as thin content.
Pages with low word count often provide less context about the topic, which can reduce their ability to rank for relevant search terms.
To fix this, consider adding more useful, relevant content to the page (often 500+ words as a general guideline).
The goal is to improve topical depth and provide clearer information for both users and search engines, although shorter content may still be appropriate for certain pages like contact pages.
Additional Reading:
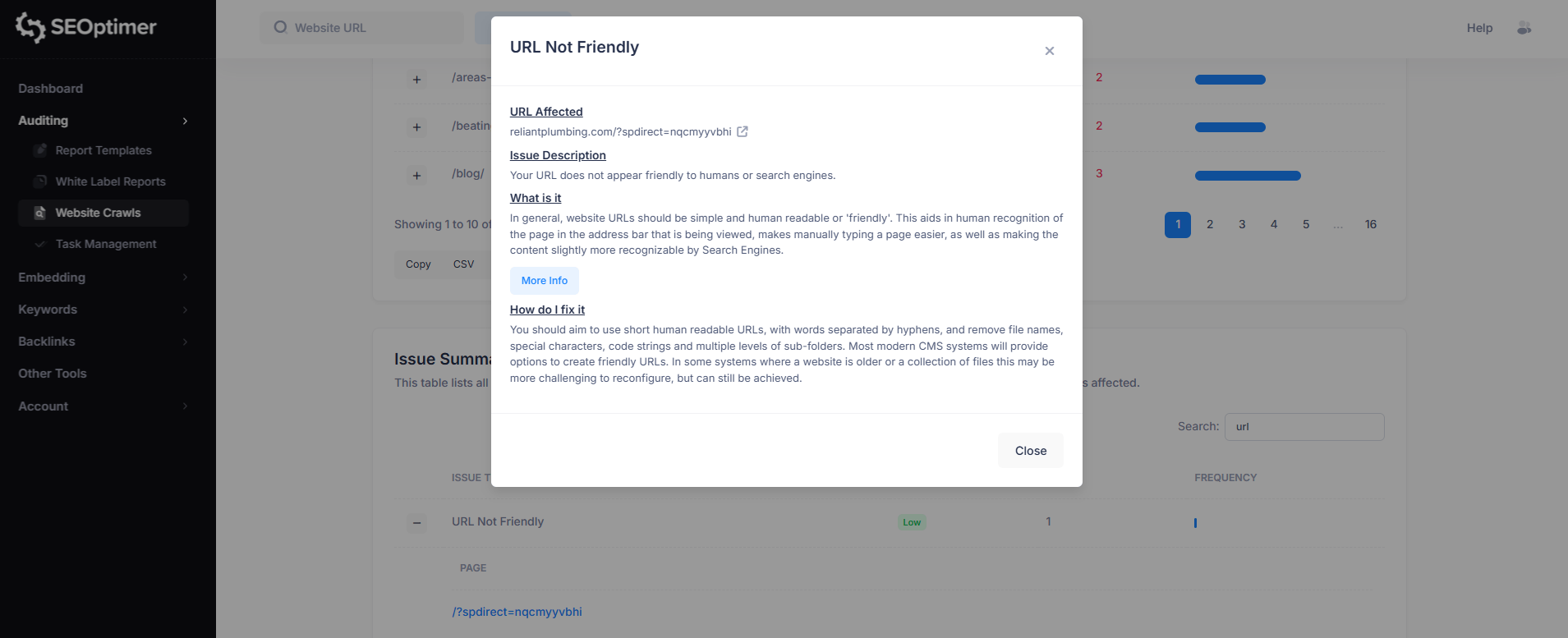
3. URL Not Friendly
Priority: Low
This issue means the page URL contains parameters or unnecessary characters that make it difficult to read and understand.
Unfriendly URLs are harder for users to recognize, less shareable, and may reduce how clearly search engines interpret the page topic.
To fix this, use short, descriptive URLs with keywords separated by hyphens, and avoid long query strings where possible.
Example:
- Unfriendly: example.com/-catering?source=pop_up&spot_id=179892&destination=catering
- Friendly: example.com/catering
Additional Reading:
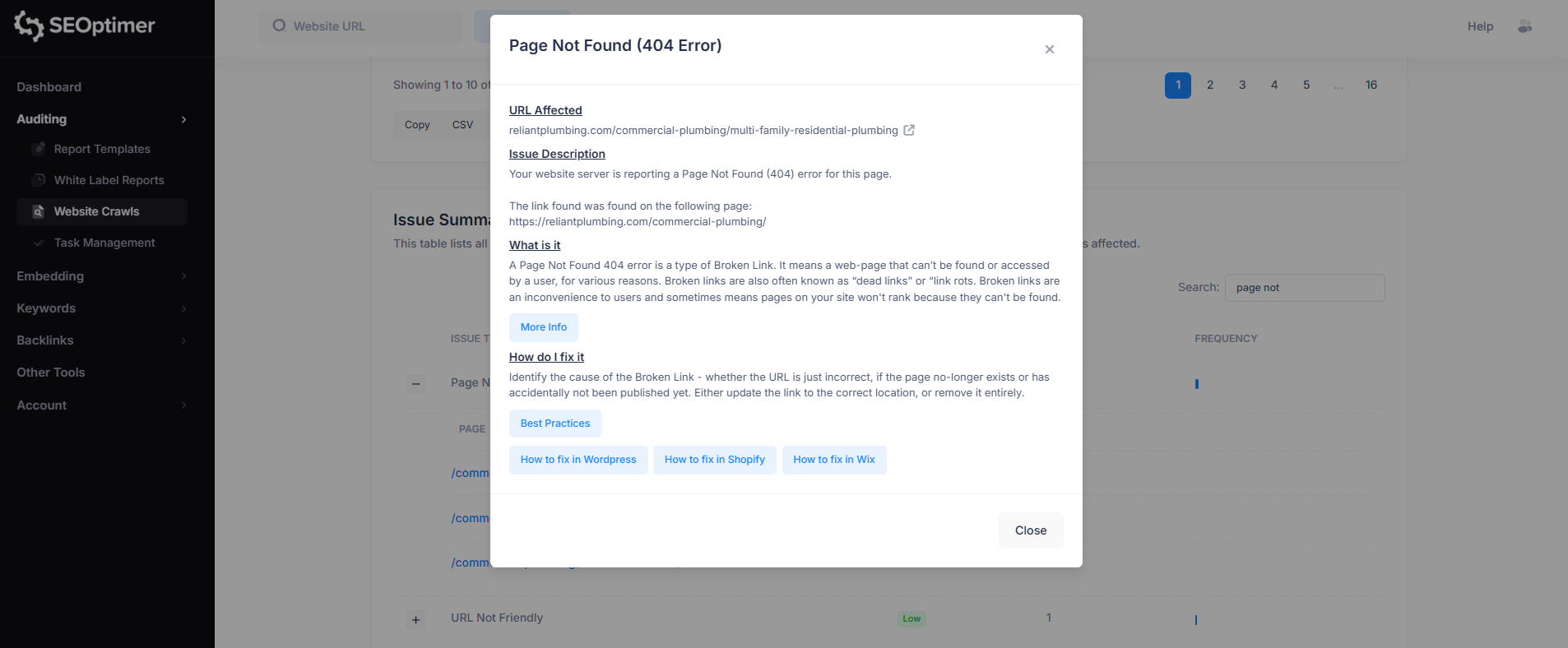
4. Page Not Found (404 Error)
Priority: High
This issue means the server returned a 404 (Page Not Found) response for the URL, indicating the page no longer exists or cannot be accessed.
404 errors often occur when pages are deleted, moved, or linked incorrectly.
To fix this, update or remove the broken link, or redirect the URL to the correct page if the content has moved.
Fixing 404 errors improves user experience and helps search engines crawl your site more effectively.
Additional Reading:
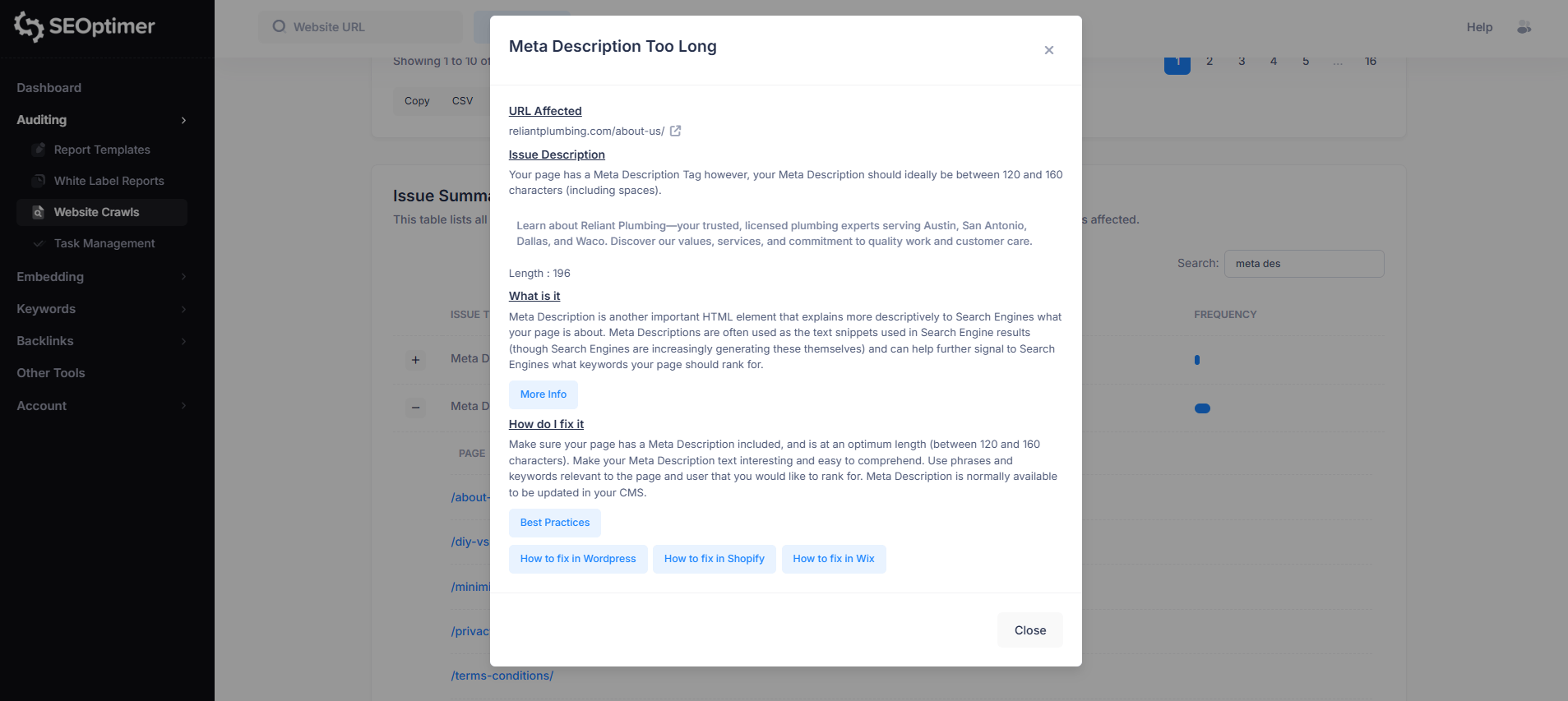
5. Meta Description Too Long
Priority: Medium
This issue means the page’s meta description is longer than the recommended length (typically 120–160 characters, including spaces).
Longer descriptions may be cut off in search results, which can reduce readability and limit how much information users see.
To fix this, shorten the meta description while keeping it clear, relevant, and keyword-focused. Meta descriptions can usually be edited in your CMS or SEO plugin settings.
Additional Reading:
6. More Than One H1 Tag
Priority: Medium
This issue means the page contains multiple H1 headings, when it is generally recommended to only use one H1 tag per page.
Having more than one H1 can make it harder for search engines to understand the main topic and structure of the page.
To fix this, ensure the page has a single clear H1 heading near the top of the content, and use H2 and H3 headings for supporting sections.
In most CMS platforms, the H1 is usually the page title or main heading.
Additional Reading:
7. Meta Description Missing
Priority: High
This issue means the page does not have a meta description tag.
Meta descriptions help summarize the page content for search engines and are often used as the snippet text shown in search results.
To fix this, add a relevant meta description that clearly describes the page and includes important keywords.
This can usually be updated in your CMS or SEO plugin settings.
8. Missing H1 Header Tag
Priority: Medium
This issue means the page does not contain an H1 heading. The H1 tag is typically the main heading of a page and helps search engines understand the primary topic and focus keywords.
To fix this, add a clear H1 heading near the top of the page content.
Each page should include one (and only one) H1 tag, which is often set automatically as the page title in most CMS platforms.
9. Poor Header Tag Usage
Priority: Medium
This issue means the page is not using multiple levels of header tags (such as H2 and H3) to structure content.
Without supporting headings, long pages can be harder for both users and search engines to scan and understand.
To fix this, add additional header levels (H2, H3, etc.) to break content into clear sections.
This improves readability and helps search engines understand the key subtopics covered on the page.
Additional Reading:
10. No Redirect to HTTPS
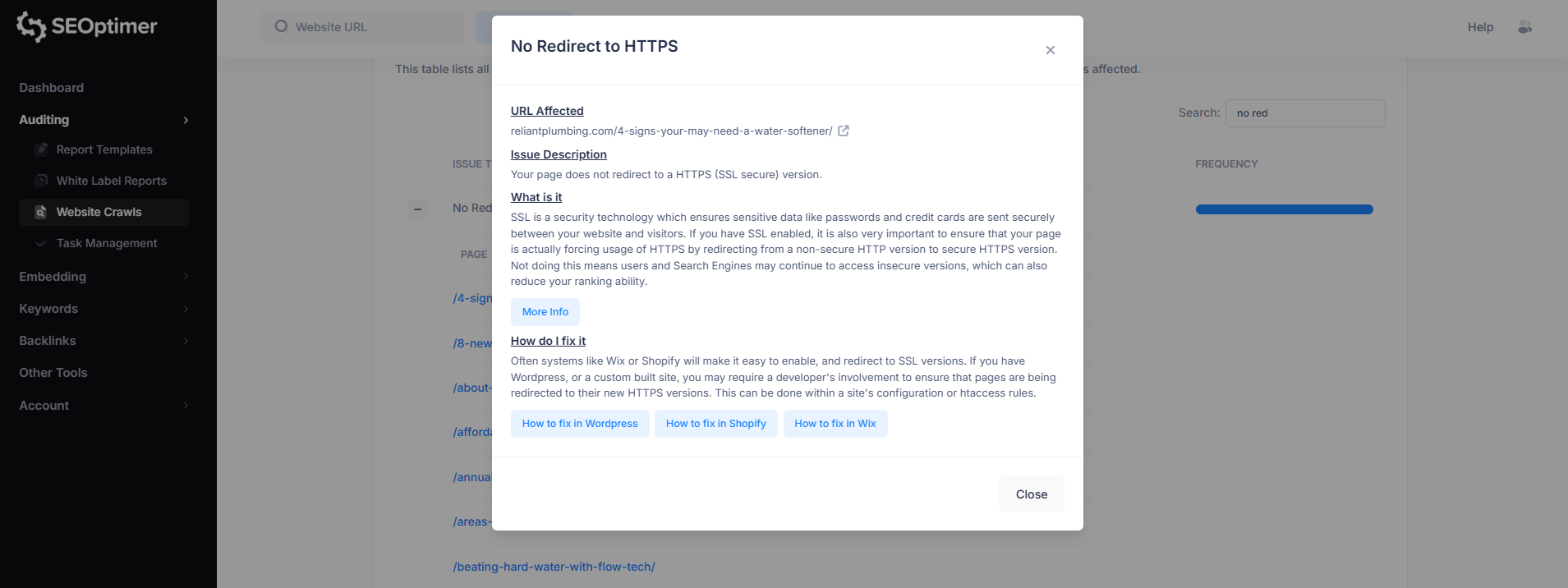
Priority: Medium
This issue means the page does not automatically redirect visitors from the non-secure HTTP version to the secure HTTPS version.
Even if SSL is installed, failing to enforce HTTPS can allow users and search engines to access an insecure version of the site.
To fix this, configure your website to force HTTPS by redirecting all HTTP URLs to HTTPS.
Many website platforms handle this automatically, but on WordPress or custom sites it may require server configuration or .htaccess rules.
Additional Reading:
Why These Issues Matter
Many SEO issues don’t affect how a website looks to users, but they can still impact how search engines crawl, interpret, and rank your pages.
A site can appear visually correct while still containing underlying technical problems such as broken links, duplicate metadata, incorrect status codes, or pages that are blocked from indexing.
These issues often become more serious as a website grows.
Small mistakes repeated across dozens or hundreds of pages can create large-scale SEO problems that reduce crawl efficiency, weaken internal linking, and prevent important pages from being discovered or ranked properly.
Identifying and fixing common crawl issues helps ensure your site is accessible to search engines, properly structured, and aligned with basic SEO best practices.
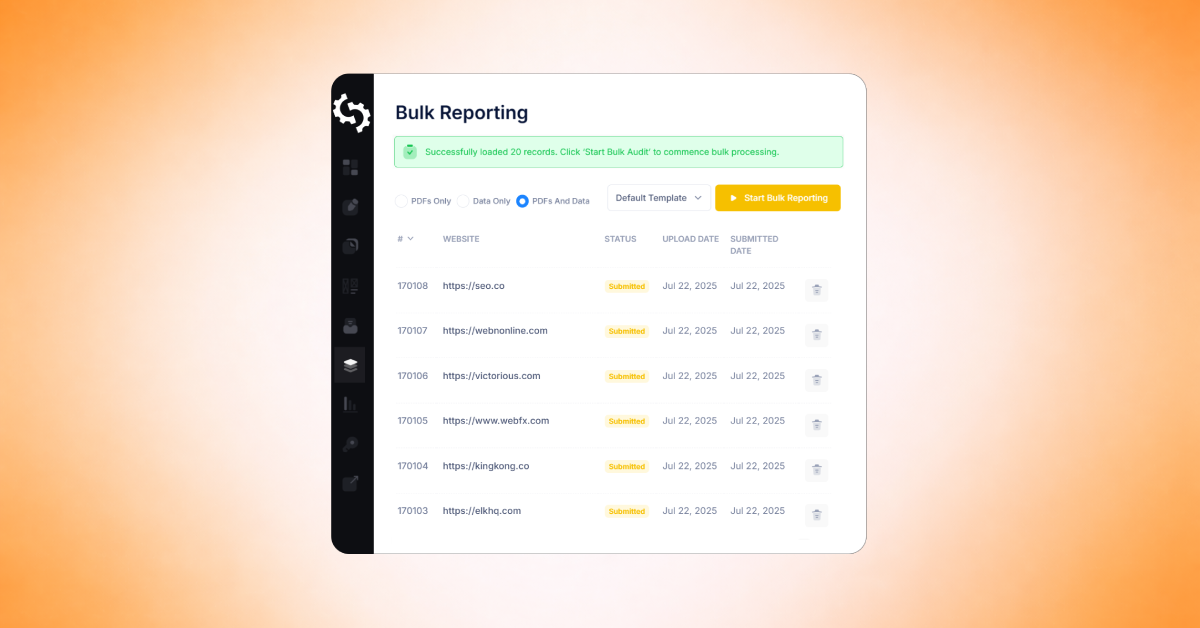
Turning Crawl Results into a Plan with Task Management
An SEO crawl can uncover a large number of issues, especially on larger websites.
While the crawl report helps identify what needs attention, the next step is turning those findings into a clear action plan.
SEOptimer’s Task Management feature helps simplify this process by converting crawl issues into a structured task list.
Instead of manually copying issues into spreadsheets or tracking fixes across multiple reports, you can manage everything in one workspace.
Tasks can be filtered by category and status, making it easier to focus on high-priority fixes first and track progress over time.
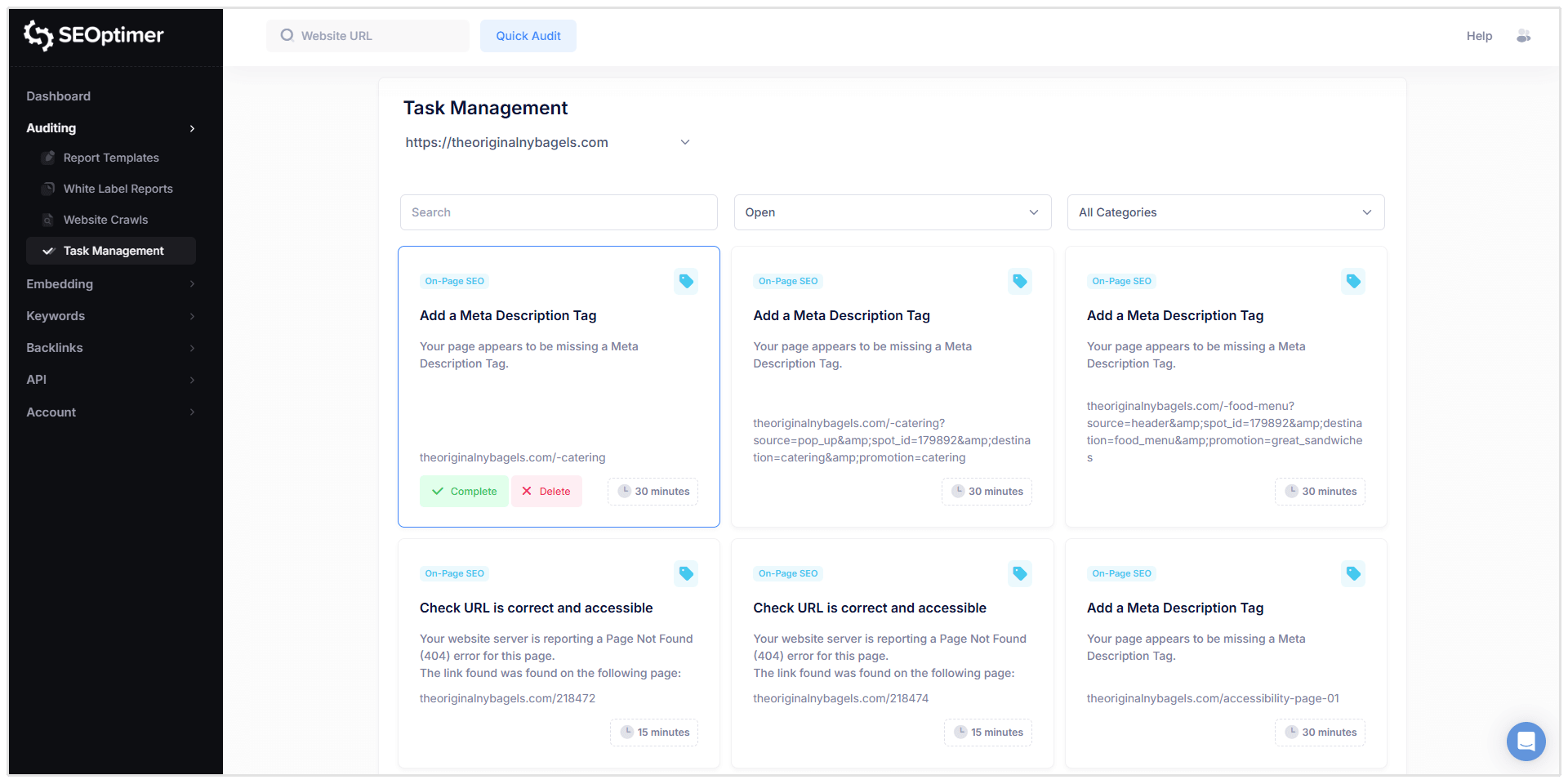
Each task includes the affected URL, issue details, and guidance on how to resolve the problem, helping you move from identifying issues to completing fixes more efficiently.
How Often Should You Crawl Your Website?
It depends on how frequently your content changes.
If your site is updated regularly, new issues can appear without being immediately noticed, such as broken links, missing metadata, or pages returning incorrect status codes.
For most websites, running a crawl on a monthly basis is a good baseline.
Larger websites, ecommerce stores, or sites that publish content frequently may benefit from weekly crawls.
SEOptimer makes this easier by allowing you to schedule crawls automatically.
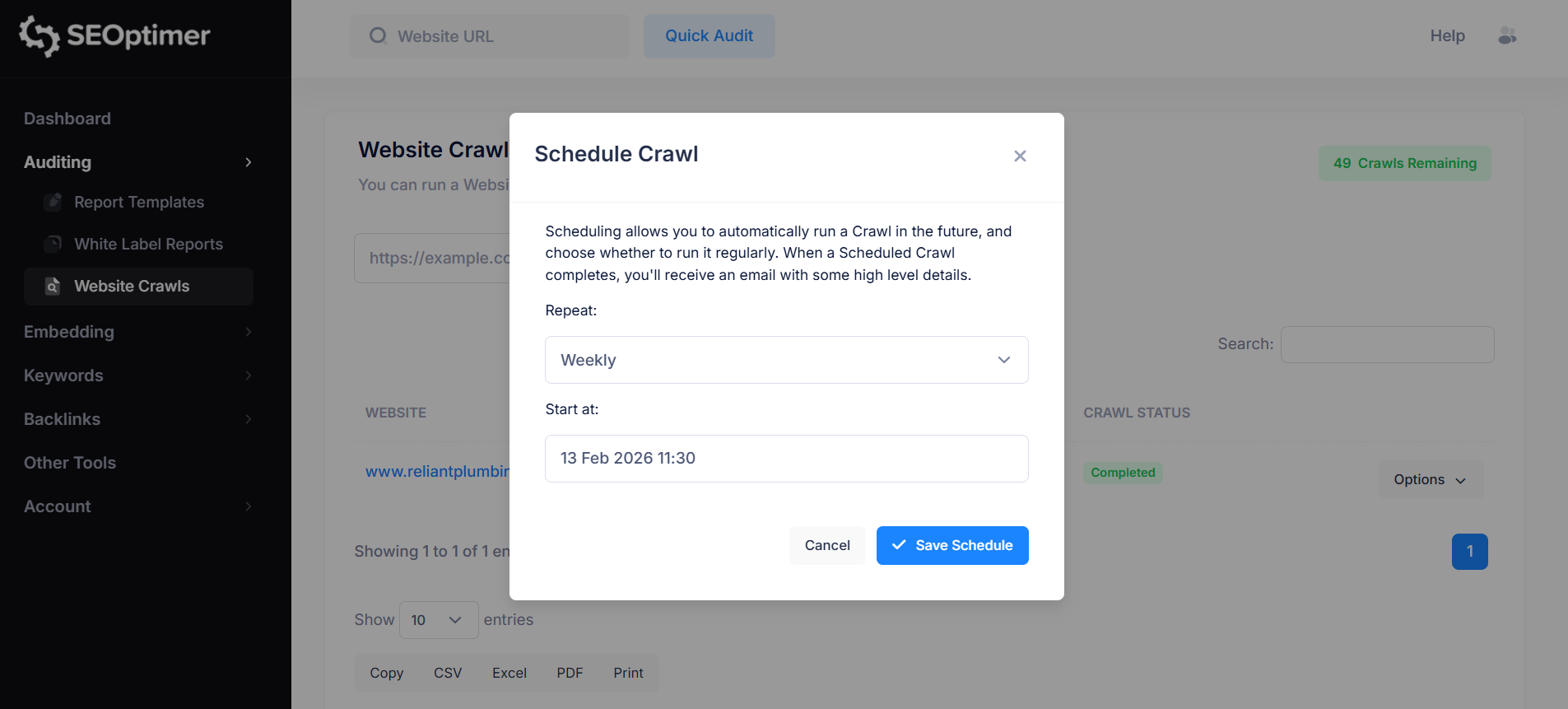
Instead of running manual audits each time, you can set up a recurring crawl schedule (such as weekly or monthly) and review updated reports as they are generated.
Wrapping Up
The issues listed above are some of the most common problems detected across SEO crawls, and they often appear across many pages on a website.
While some may seem minor on their own, fixing them can improve crawlability, page structure, and overall search visibility.
Running regular crawls helps you catch these issues early and track improvements over time. Once a crawl is complete, you can use the SEOptimer crawl report and Task Management feature to prioritize fixes and work through issues systematically.
Need Help?
Live Chat: Click Live Chat (bottom right)
Email: [email protected]
Response time: Within 24 hours


.png)