What is a Title Tag?
A title tag is a piece of HTML code located in the <head> element that tells search engine users what the topic of the webpage is.
The title tag is also one of the most important on-page SEO factors.
Where Can You See the Title Tag?
You can view the title tag of any web page by simply right-clicking anywhere on the page and selecting “Inspect Element” or “View Page Source”.
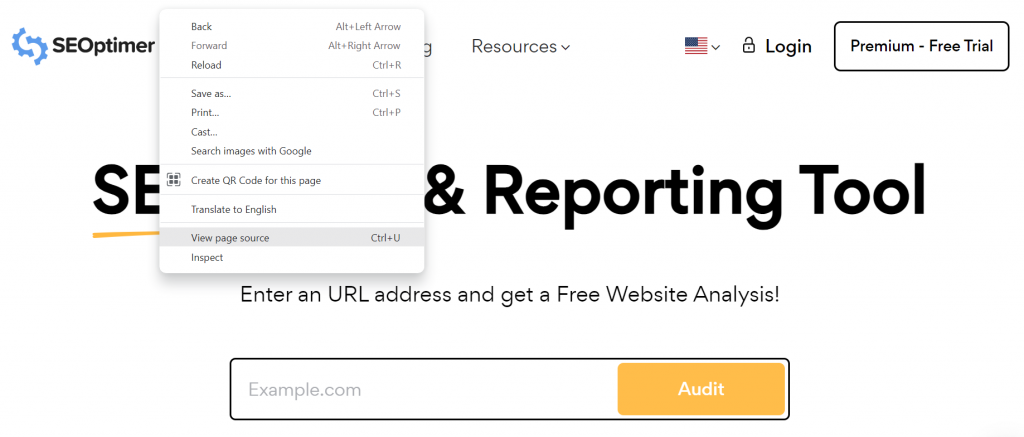
Then, search for “<title>” to see the title tag.
<head>
<title>Analyze Websites With Free SEO Audit & Reporting Tool - SEOptimer</title>
</head>
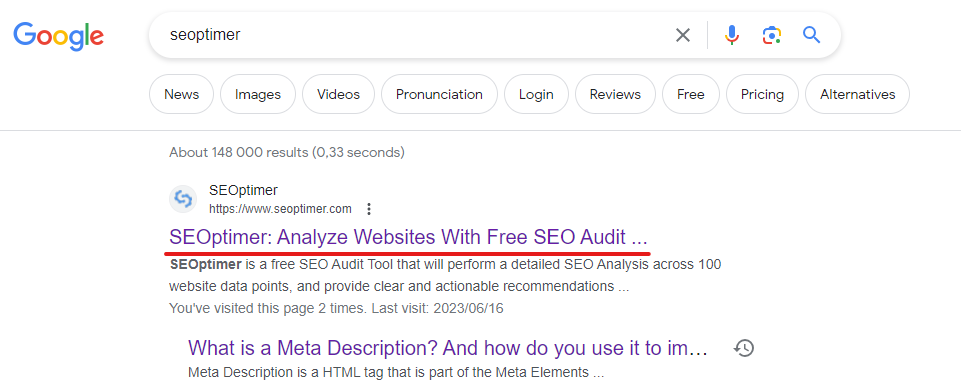
The title tag is prominently featured as a clickable link in search engine results pages (SERPs):
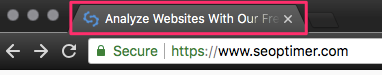
An HTML title tag can appear in three additional areas even though you or your visitors might not see the actual HTML <title> code unless they view the page source.
Those areas are:
- In your browser toolbar when you are on the actual site
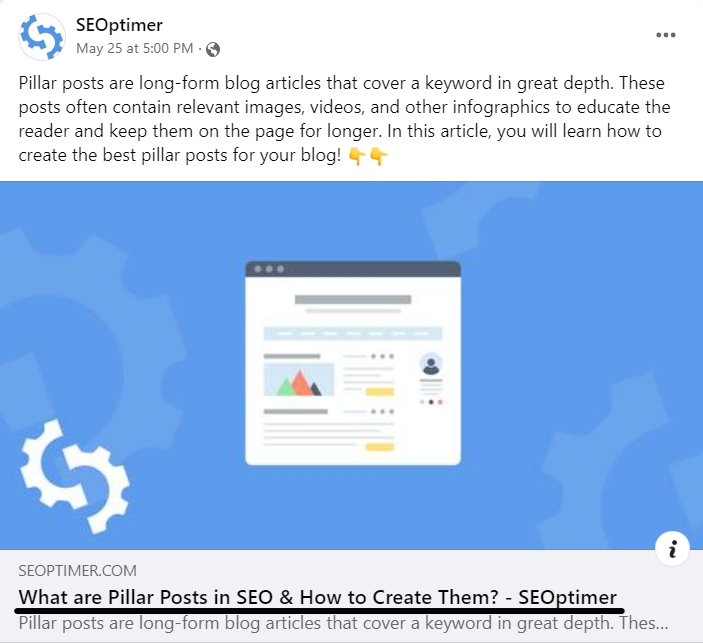
- In your bookmarks if you’ve bookmarked the page

- On social networks when you share the link to that page
Why is the Title Tag Important?
The title tag is the primary piece of information you can give search engine users to help them decide which SERP results they should click on. It’s important to write high-quality and accurate titles relevant to what your ideal audience might type into Google.
If you search “SEO audit tool” (singular) versus “SEO audit tools” (plural), you might receive two different results.
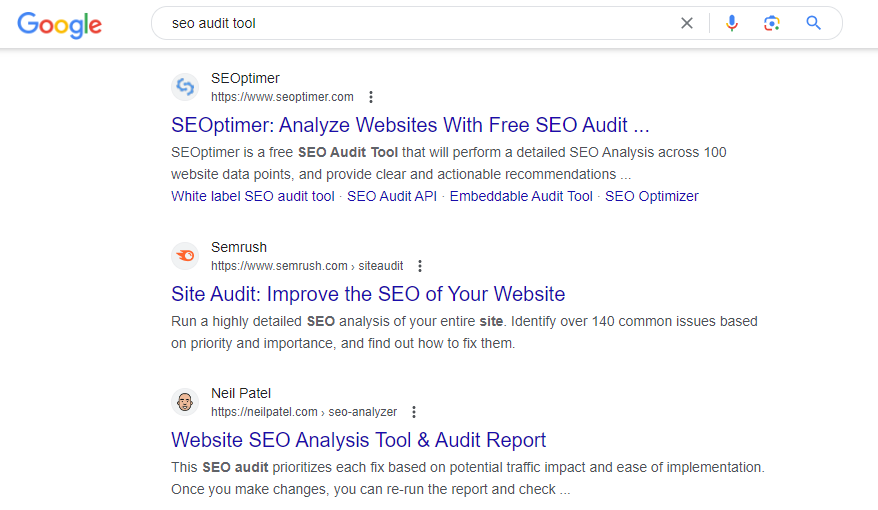
One of the results may provide a list of software tools that provide “SEO auditing” services and the other a list of articles featuring top SEO audit tools you can use.
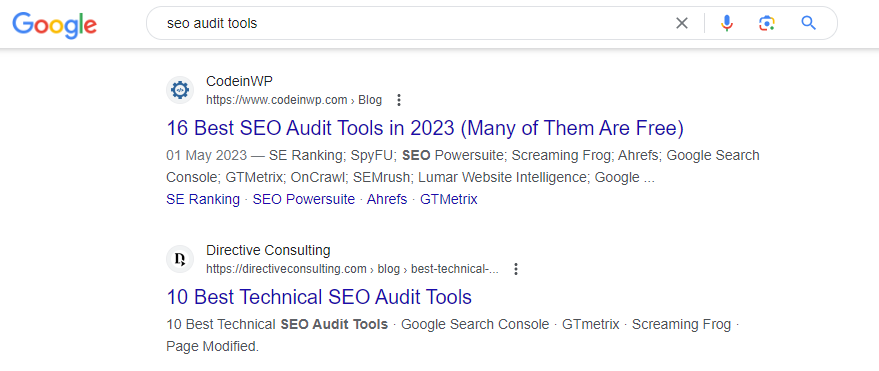
More importantly, the title tag is used as a ranking factor for Google.
“We do use the title tag for ranking, but it’s not the most critical part of a page. So it’s not worthwhile filling it with keywords to kind of hope that it works that way.” - John Mueller
He later mentions in a 2018 Reddit article:
“Good titles & descriptions are some of the easiest wins you can get on web pages…How are search engines supposed to guess what you want your pages to rank for?”
Why Does Google Change Your Title in the SERPs?
One of the foundational elements of SEO is creating title tags that accurately represent and describe how your content relates to your user’s query. Search engine bot crawlers will first check the site’s HTML <head> element to understand what your content is about.
However, if your title tag is not accurately portraying your content and does not follow Google’s guidelines, they may try to generate an improved title from other sources, like anchors or on-page text.
When search engines know the user’s query, they will try to figure out why the results (i.e., your page) are relevant by pulling from elements within the page or from the alternative text.
The most important thing to remember is to create title tags that are tailored for the target search query. Creating title tags with the end-user in mind can increase the chances of higher rankings and improved click-through rates.
How to Create an SEO-Friendly Title Tag
To create the most effective title for your site, you need to follow certain guidelines. There are a few things to keep in mind in order to create creative and click-worthy page title tags:
Title Tag Length
Let’s find out how long your title tag should be.
There are several well-known sites that have tested the limits to how long a title tag should be:
- W3.org suggests that title tags should ideally be less than 64 characters in length.
- According to Moz, a title tag should ideally be 50–60 characters.
- At SEJ, 64–70 characters are recommended, depending on your word breaks.
- Wix, a popular website builder, recommends that you keep your title between 55–60 characters.
Based on our findings and other research, you should ideally keep your title tags between 50 to 55 characters in length. This will ensure that Google doesn’t truncate the title tag and that search engine users will be able to see your entire title in the SERPs.
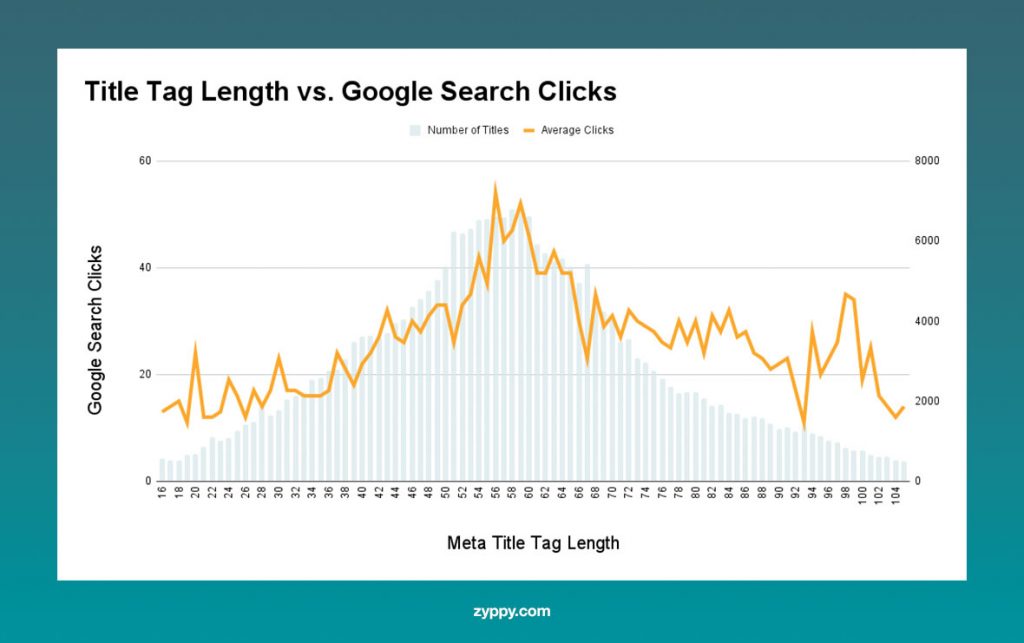
Image source: Zyppy
One way to ensure that title tags are as short and succinct as possible is to eliminate the use of unnecessary words and descriptors.
Avoid using ambiguous descriptors like “Home” for your homepage or “Profile” for a particular user’s profile as these take up unnecessary characters in the title tag.
Furthermore, avoid using all “stop words” such as “the”, “to”, and “in”.
Avoid Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing is the practice of filling your title with keywords in an attempt to manipulate your site ranking. Here is an example of obvious keyword stuffing:
“How-to SEO: Your Ultimate SEO Guide for Your SEO Needs”.
Titles like this are spammy and result in a poor overall user experience. Instead, focus on generating helpful and informative titles that make use of the keyword in the most natural way.
With the introduction of the Helpful Content updates, Google is more focused on rewarding websites that write for humans instead of for search engines. Always write content and titles for the reader, not for the search engine.
Boilerplate or Repetitive Keywords
It’s important to have clear-cut titles for every page on your site that will accurately describe the content of those pages. Don’t use titles that will make it difficult for users to distinguish one page from another.
For example, adding the phrase “Best dating tips” to every page title on a dating site makes it very difficult for users to differentiate how one page differs from another.
Uninformative page titles should be redeveloped to accurately reflect the content of each page.
In our dating site example, terms such as “Tips”, “Pick up lines”, “Conversation starters”, and “Quotes” should not be included on every page, even though all of these terms are relevant to the website.
You should only include the keywords in the title if the page actually discusses these topics.
Add the Target Keyword to Titles
Another essential part of creating SEO-friendly page titles is to always remember to include the page’s target keyword as close to the beginning of the title as possible.
The reason for this is two-fold:
- Adding the target keyword to the title will give search engines even more information about your page, making it possible for them to rank the page for the appropriate queries.
- Whenever a human sees a search result that contains the phrases and keywords that match their search query, they are more likely to click on it.
How to See Your Title Tags in Google Bing?
Once you’ve created your title tag and after Google has indexed your page, you’ll want to see how it actually shows up on Google.
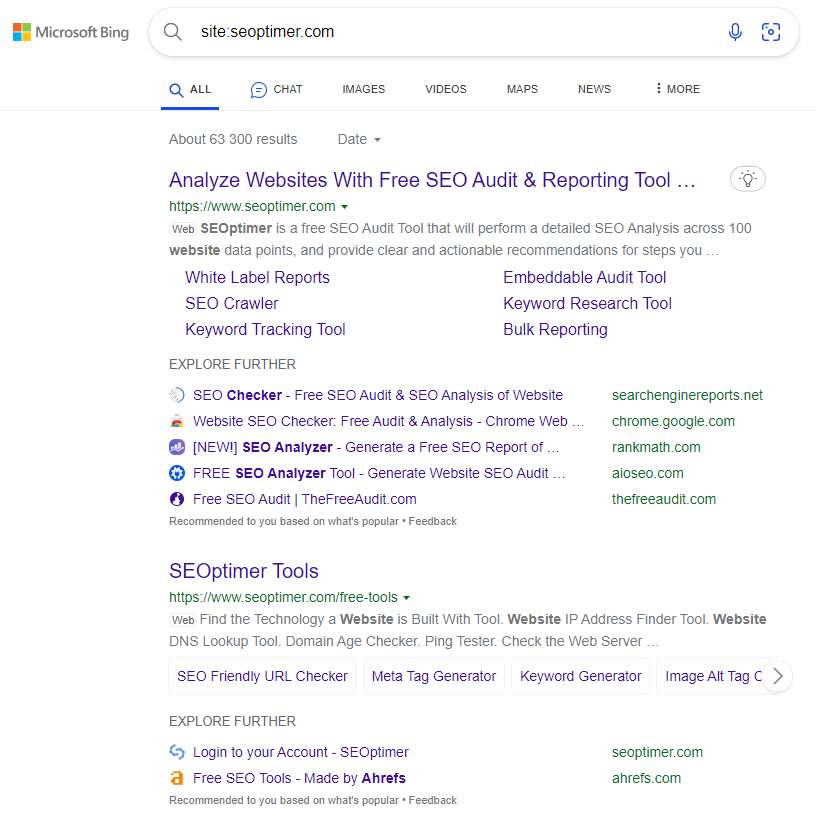
You can type in “site:www.yoursite.com” on either Google or Bing and see each page that has been indexed. Make sure not to insert a space between “site:” and “www.yoursite.com”.
Here’s a Bing example:
What to Do if Google Doesn’t Show an Updated Title?
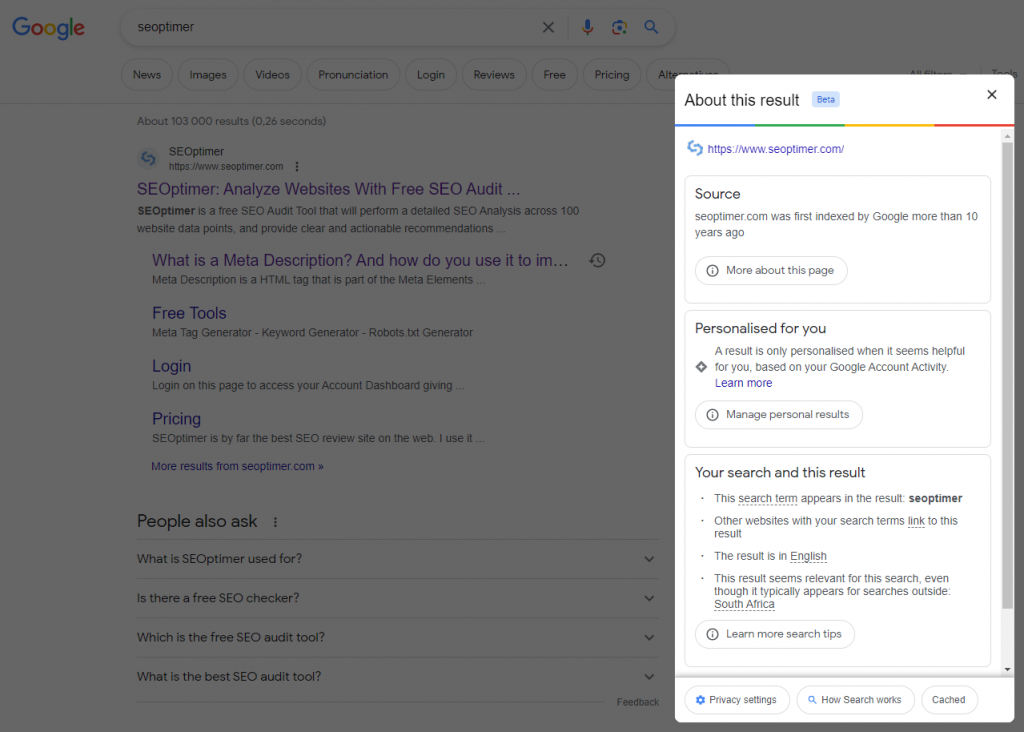
Google might not show the updated page title because your site SERP information might be cached. Check the Google Cached link by clicking on the three dots next to your search result to see which page Google is using for your page.
More than likely, Google hasn’t crawled your site and or noticed the changes you’ve made.
You can try logging in to Google Search Console and submitting your URL under URL inspection > Request Indexing.
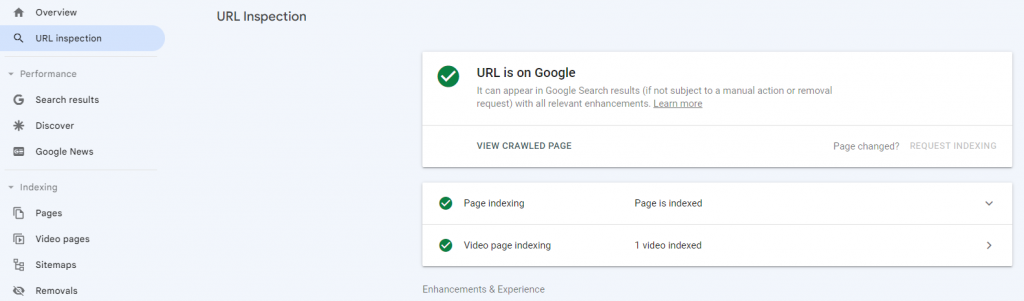
This will tell Google to index the updated version of the specific page.
Conclusion
We learned what a title tag is and why it is important for SEO. It’s one of the easiest wins in SEO but few people know how to create titles that are optimized for search engines.
We also learned the difference between a meta title and a title tag, along with best practices to help you optimize your site's SEO.










