Key Takeaways
- SERP features now dominate above-the-fold visibility and reduce organic CTR.
- Content that’s structured, concise, and easy to extract wins more SERP features.
- The same techniques used to win featured snippets also help you get cited in AI Overviews.
Maps, images, question boxes, and AI answers often appear before the first organic result, pushing traditional listings further down the page. If you want to stay visible in modern search results, you need understand how to get into SERP features and optimize for them.
The good news? Getting into SERP features is about structuring your content so it’s easy to extract, easy to trust, and clearly the best answer to a specific query.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to get your articles and pages into SERP features and win more visibility across Google’s most common placements.
What are SERP Features?
SERP features are any results on a Google Search Engine Results Page that are not traditional organic results.
In the early days of Google, a results page was simply ten blue links, some ads, and maybe even some images.
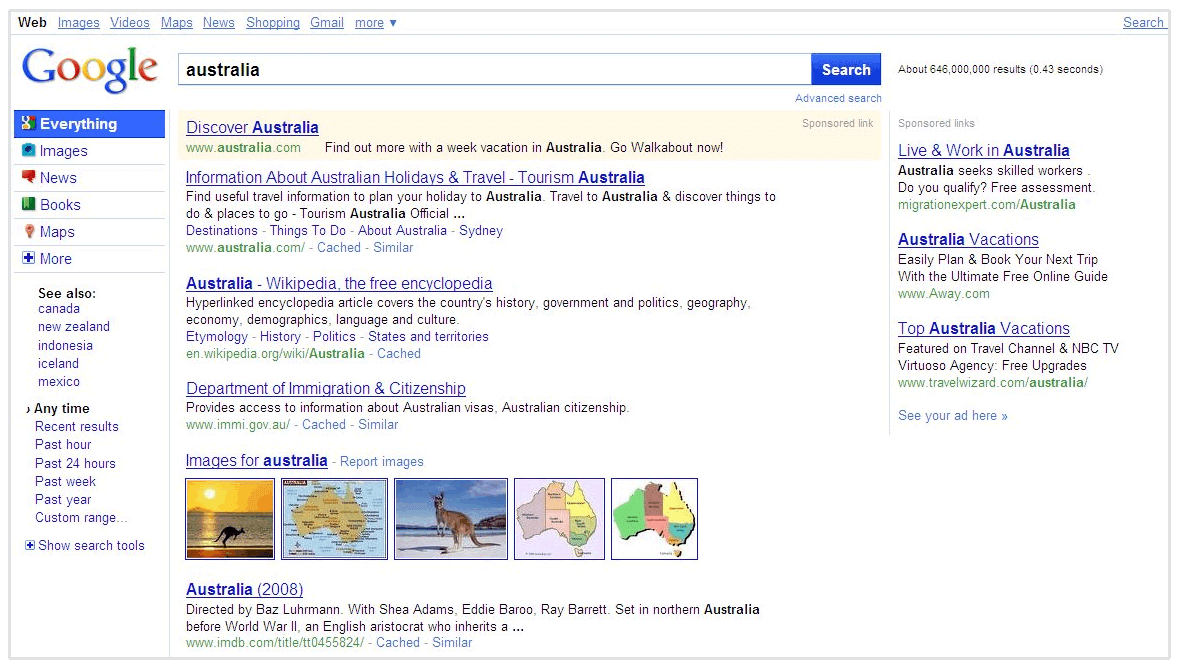
Today, Google tries to answer the user's query as quickly and visually as possible. To do this, they pull data from websites and display it directly on the results page.
Examples of SERP features include:
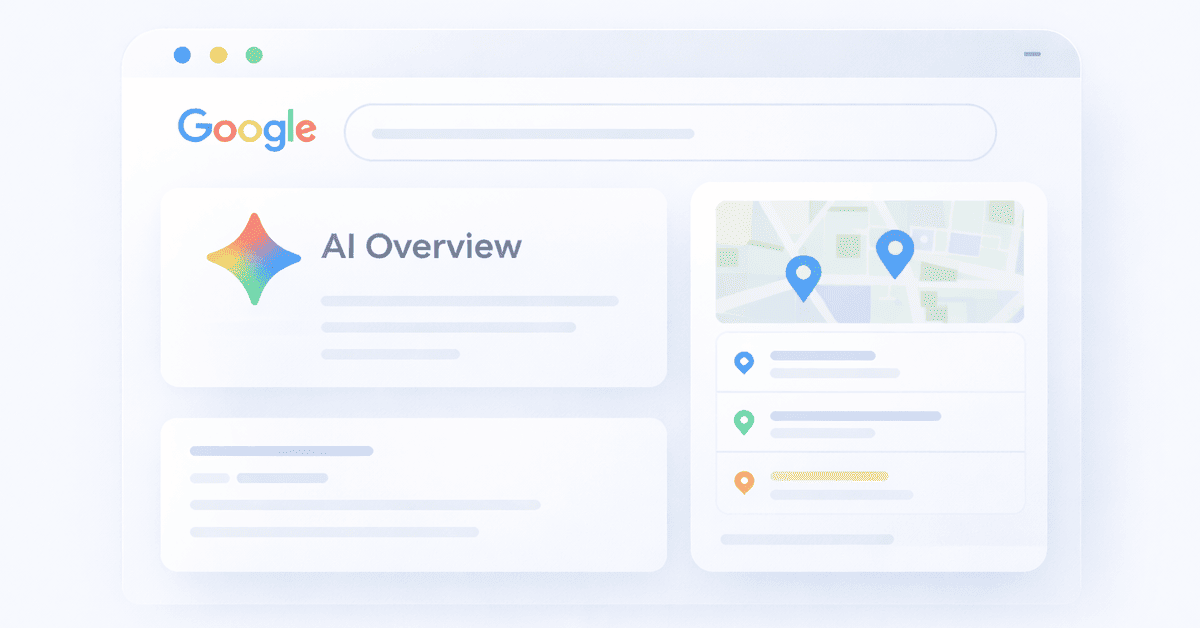
- AI Overviews: An AI-generated summary that synthesizes information from multiple sources and appears at the top of the results page.
- Featured Snippets: A block of text at the very top of the page answering a question.
- Local Map Pack: A map showing three local businesses.
- Image Pack: A row of images relevant to the search.
- People Also Ask (PAA): A list of related questions users can expand.
Why do these matter?
Because these SERP features steal attention and clicks.
Take AI Overviews as an example, according to data from Seer Interactive, organic CTR on informational queries fell from 1.41% to 0.64% year over year when AI Overviews were present (a decline of more than 60%).
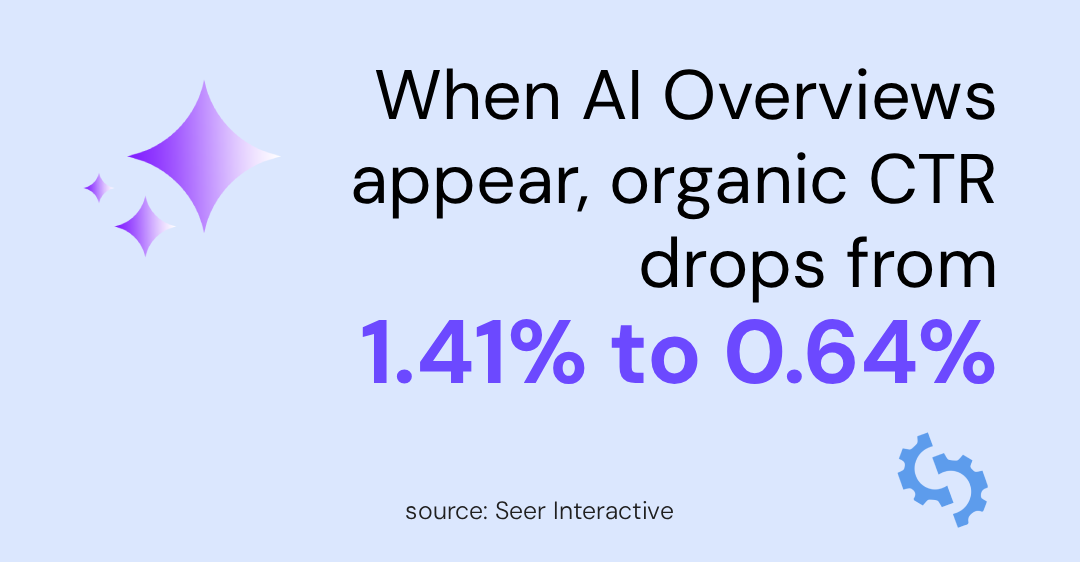
They also found that when you are cited in an AI Overview, you get 35% more organic clicks compared to when you are not cited at all.
So smart marketers and SEOs should not only focus on optimizing for traditional blue links, but also for the SERP features and AI-driven results that now take up a significant portion of real estate in Google search results.
Different Types of SERP Features
To get into SERP features, you first need to understand what you are aiming for.
Google offers dozens of features, but these are the SERP features that content marketers and SEOs should focus on.
AI Overviews
The newest addition to the SERP is the AI Overview (formerly SGE).
This feature uses generative AI to synthesize information from multiple sources into a coherent summary.
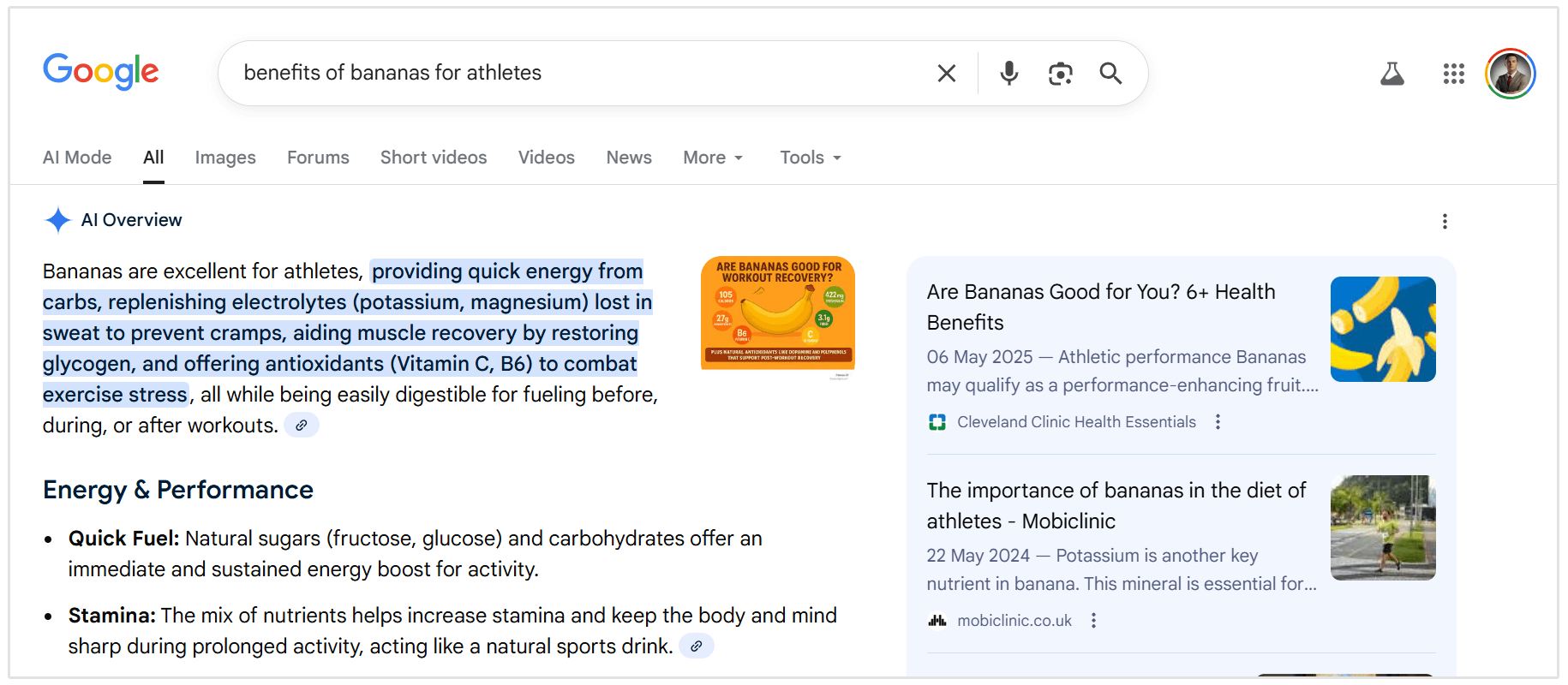
While it pushes organic results further down, Google often cites the sources it used to generate the answer, providing a new way to gain visibility.
Featured Snippets
Before AI Overviews, there was Featured Snippets. And while Google hasn't confirmed that this SERP feature is dead, Featured Snippets are far less common that they were pre-AI Overivews.
SERP tracking from Ahrefs shows that Featured Snippet visibility declined from 15.41% of queries in January 2025 to 5.53% by June, a drop of around 64% as AI Overviews expanded rapidly.
When both features are plotted together, there is a clear “switch-over” point in March, when AI Overviews grew by 116% and Featured Snippets declined heavily.
That doesn’t mean featured snippets are obsolete.
While they now appear far less frequently, they still surface on narrow, factual queries where a single clear answer exists. When they do appear, they remain one of the most visible and valuable placements on the SERPs.
A Featured Snippet appears at position zero, right below the ads but above organic results. It usually provides a direct, concise answer to a user's question.
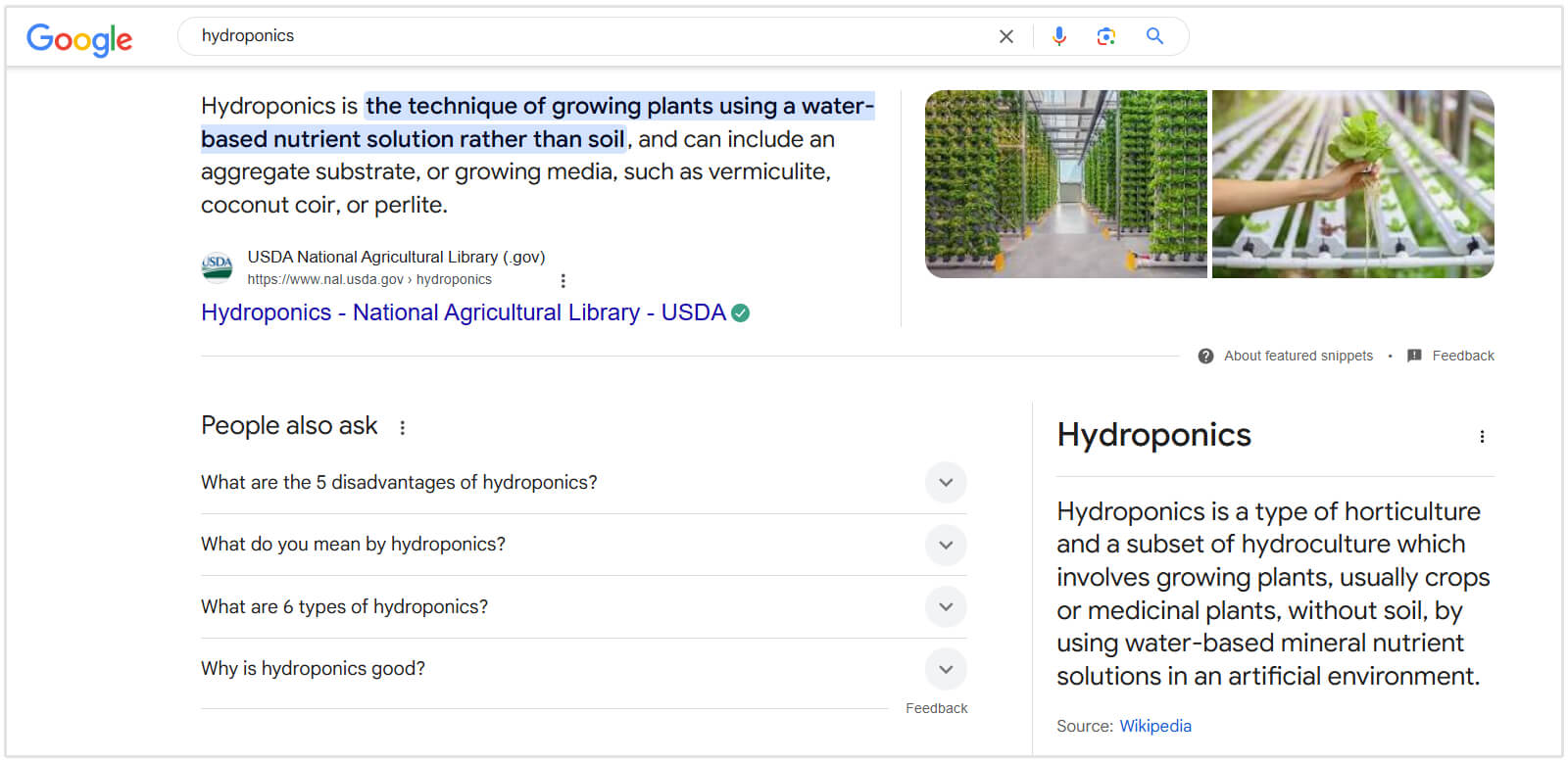
Snippets come in three main formats:
- Paragraph: A short definition or answer.
- List: A bulleted or numbered list (great for recipes or "best of" lists).
- Table: Data organized in rows and columns.
Local Pack
If you have ever searched for "pizza near me" or "plumber in seattle," you have seen the Local Pack.
It displays a map and three business listings with reviews, hours, and contact info.
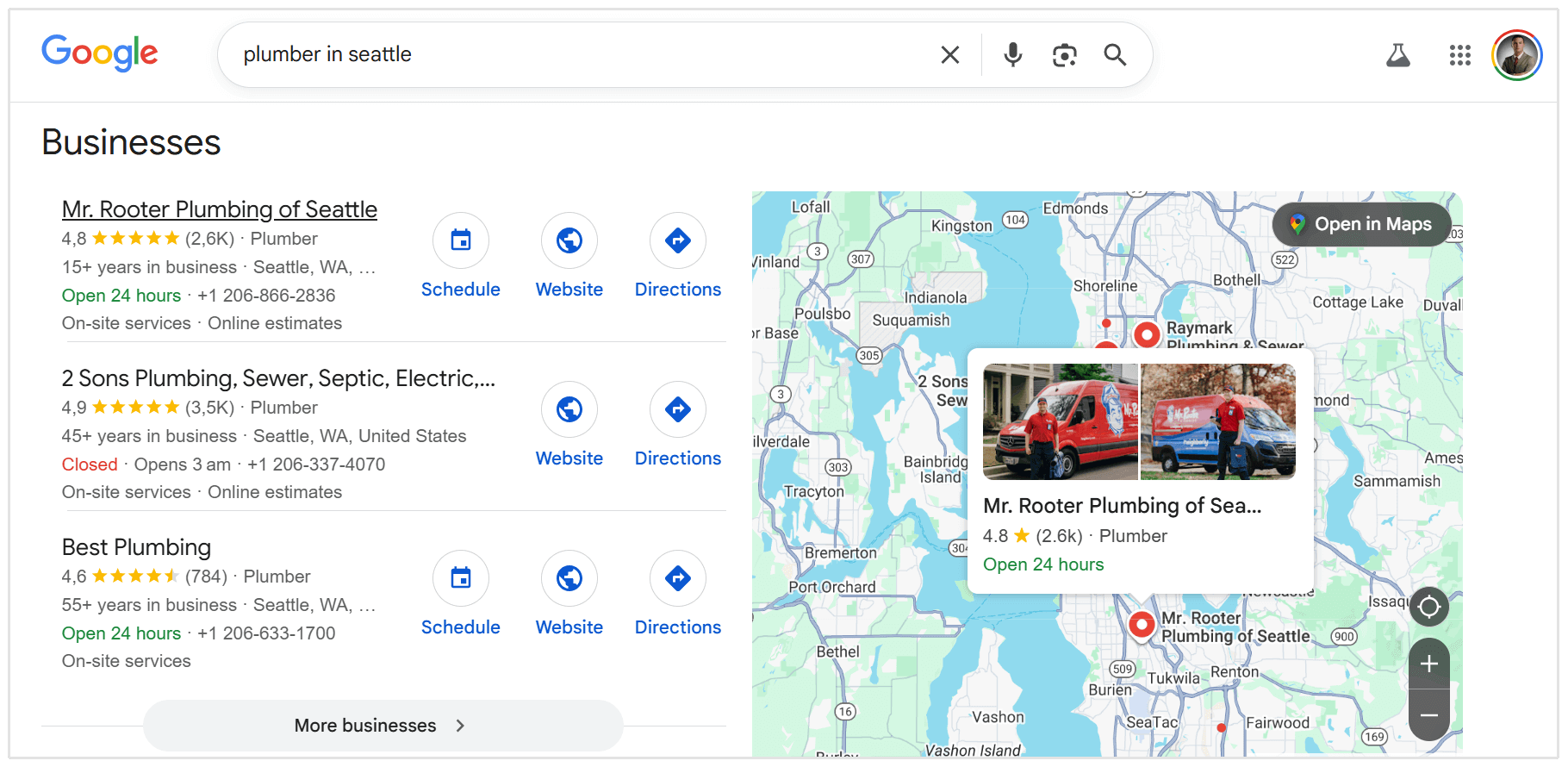
For local businesses, this is often more valuable than a standard website ranking because it captures high-intent users ready to visit or call.
Knowledge Panel
These are the large boxes that appear on the right-hand side of desktop results (or top of mobile).
They provide encyclopedic information about entities—people, organizations, places, or things.
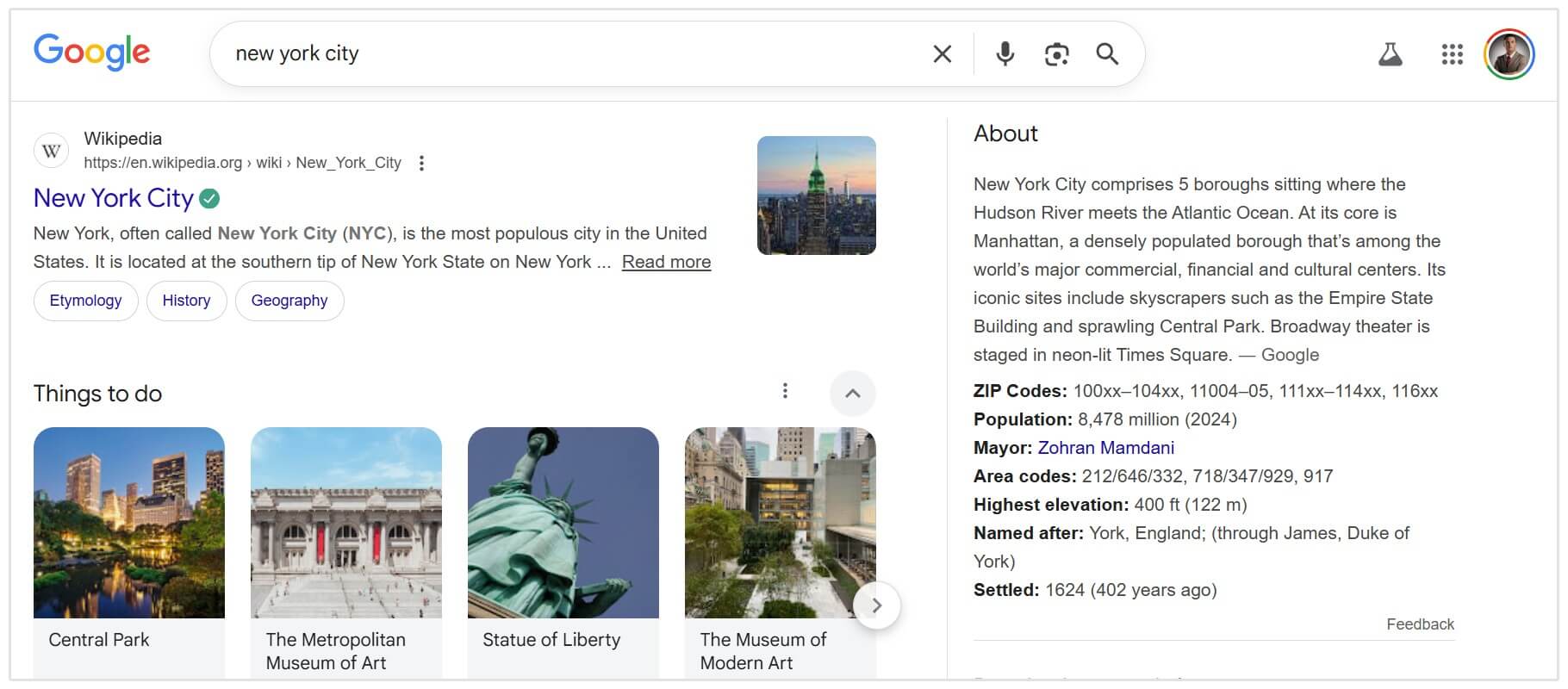
Google usually pulls this data from trusted sources like Wikipedia, LinkedIn, and its own Knowledge Graph.
Image Pack and Video Carousel
Visual search is massive.
If you search for "red Nike shoes" or "kitchen tile ideas," Google knows you want to visually see options, not just read about them.
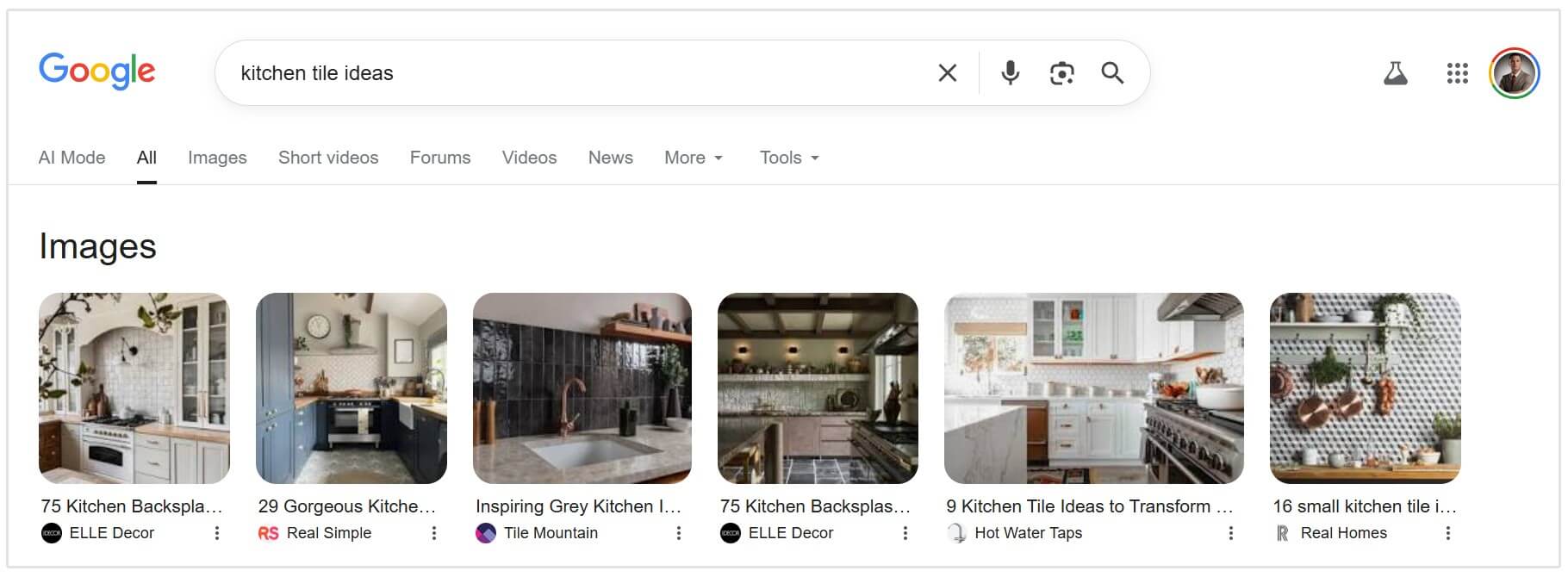
For how-to queries like "how to tie a tie," Google often displays a carousel of YouTube videos, sometimes even highlighting specific key moments within the clip.
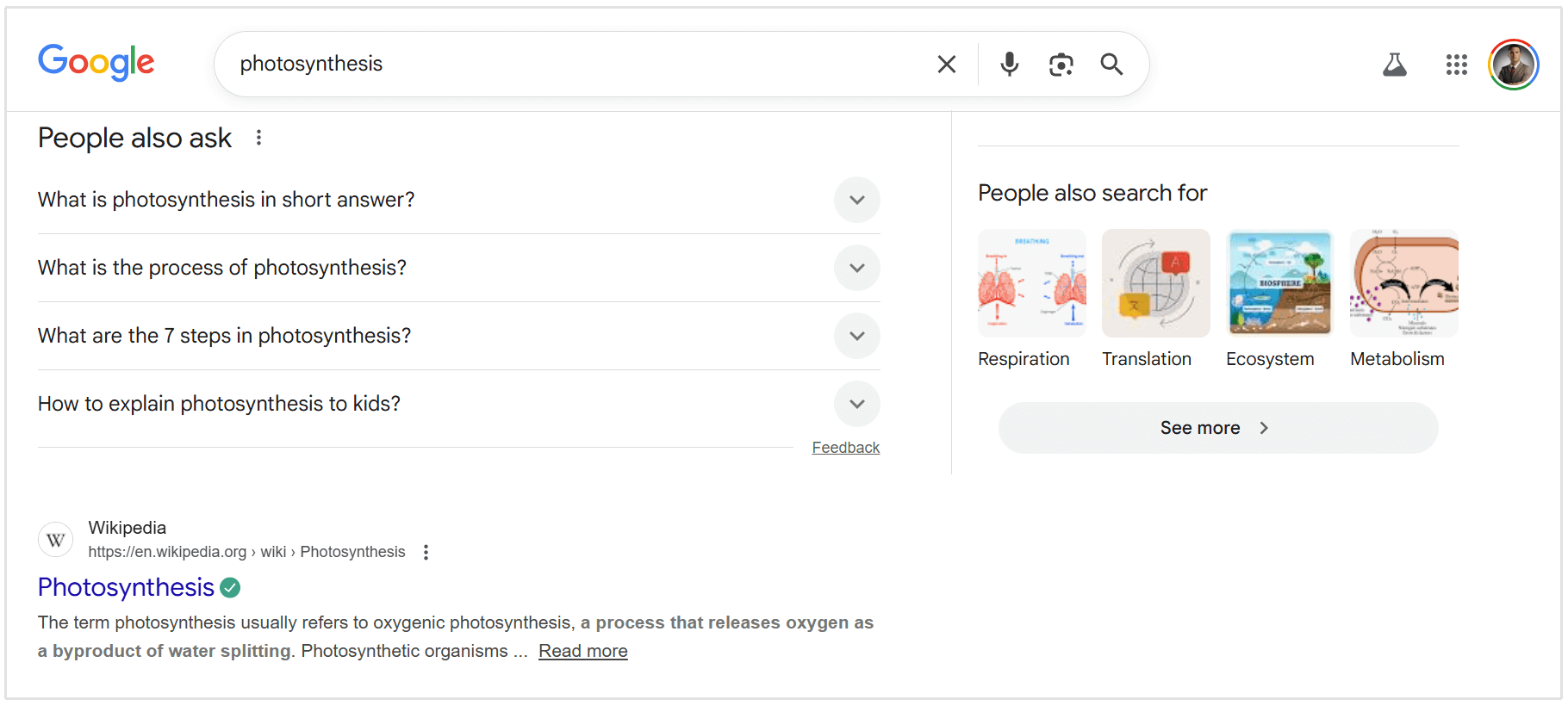
Google People Also Asked Questions
People Also Ask boxes show a list of related questions that expand to reveal short answers pulled from web pages.
These questions often appear near the top of the results and can repeat multiple times as users expand them.
Now that you know some of the most common SERP features, let’s take a closer look at how to get into them.
How to Get Into AI Overviews
AI Overviews represent a major shift in how Google serves information and how users behave on search results pages.
The rise of AI-generated summaries has coincided with a significant increase in zero-click searches.
Broader trend data from Similarweb shows that zero-click searches climbed from around 56% to 69% between 2024 and 2025, a period that aligns with the rollout of AI Overviews.
This shift is also visible in direct click behavior.
Pew Research tracked 68,000 real search queries and found that when an AI summary appeared, users clicked a result only 8% of the time compared to 15% when no AI summary was shown.
While Google hasn’t published a “how-to” for getting included in these overviews, early evidence and industry analysis suggest the strategies below can improve your chances of being cited in AI summaries:
- Be the Primary Source: AI models prioritize authoritative sources. Original research, unique data, and expert interviews are more likely to be cited than rehashed content.
- Focus on Conversational Language: The AI mimics natural language. Content written in a clear, conversational tone is easier for the LLM (Large Language Model) to digest and summarize.
- Cover the "Next" Question: AI Overviews often try to anticipate follow-up questions. If your article covers the main topic plus the logical next steps, you increase your chances of being included.
Landon Murie from Goodjuju Marketing summarizes getting into AI Overviews as such:
Content needs to be nicely organized and offer quick answers to visitor questions (best in 40-60 words right beneath each question-based subheading).
- Landon Murie, CEO of Goodjuju Marketing
Related Reading: How to Rank in AI Overviews (with Insights from Top SEO Experts)
How to Win Featured Snippets
As we established earlier, featured snippets are far less common than they were before the rollout of AI Overviews.
Google now shows them more selectively, and many queries that once triggered snippets now surface AI-generated answers instead.
That said, featured snippets are still worth targeting.
Not only because they occasionally appear on narrow, factual queries, but because the same techniques used to win snippets are increasingly used by Google to source content for AI Overviews and other SERP features.
In practice, learning how to win featured snippets is one of the best ways to optimize for modern answer-based search.
When featured snippets do appear, winning one is often one of the fastest ways to increase your visibility.
Pick Snippet-Friendly Query Patterns
You need to target queries that demand a specific, extractable answer. Look for keywords starting with:
- "What is..."
- "How to..."
- "Best [product] for..."
- "Benefits of..."
- "Difference between X and Y"
Use keyword research tools to find the search volumes and study the competitive landscape for many of these types of queries.
Build the "Snippet Block"
Google's bot is smart, but you need to make its job easy. You should create a specific section in your post designed to be "snippable."
If you are targeting the keyword "what is content marketing," do not bury the definition in the third paragraph.
Instead use the following framework to create the section you want featured in the snippet:
- Ask the question: Use an H2 or H3 header that matches the query exactly (e.g., <h2>What is Content Marketing?</h2>).
- Answer immediately: The text directly below that header should be a concise, 40-60 word definition.
- Keep it objective: Avoid fluff or opinion in this specific block. Stick to the facts.
Like this below example from Shopify, it has a heading and directly answers the question of "What is content marketing?," avoiding any fluff or opinions:
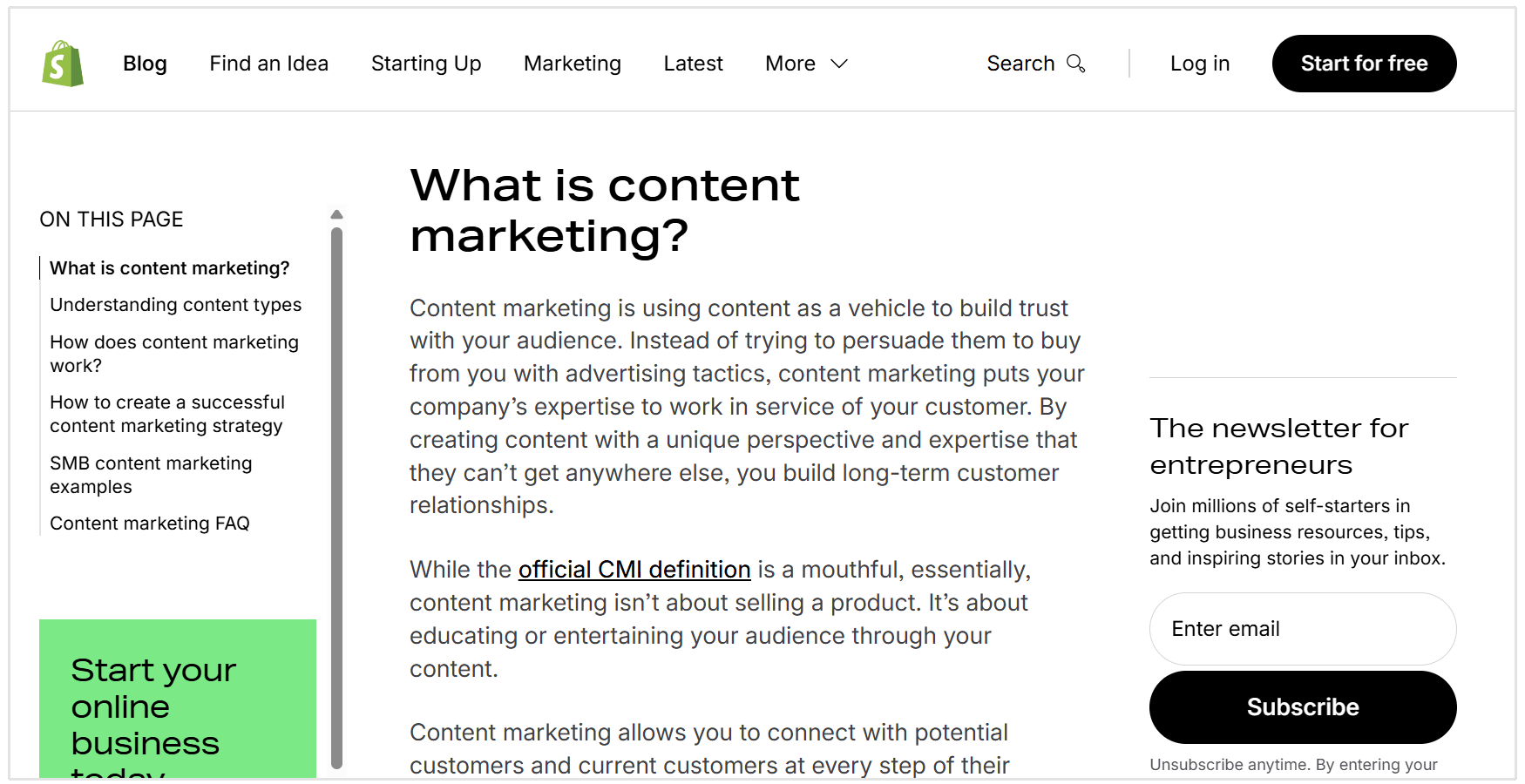
On-Page Layout that Commonly Wins
The format of your answer must match the format Google wants to show.
- For Definition Snippets: Use a clear, short paragraph (<p> tags).
- For List Snippets: Use HTML list tags (<ol> or <ul>). If you are writing a "how-to" guide, ensure every step is an H3 header, or wrap the steps in a list format.
- For Table Snippets: Use clean HTML table tags (<table>). Don't rely on CSS to make a div look like a table; use the actual table structure.
How to Get into PAA
Beyond AI Overviews and Featured Snippets, there are other ways to get your articles in SERP features like People Also Ask (PAA).
Mine PAA Questions
The "People Also Ask" box is a goldmine for content ideas. Google is literally telling you what related questions users have.
To capture these:
- Search for your main keyword.
- Look at the PAA box. Click on a few questions (this often triggers Google to load even more questions).
- Copy these questions.
- Add an FAQ section to your article or integrate these questions as H2/H3 headers within your content.
Write "Micro Answers" under Question Headings
Just like with Featured Snippets and AI Overviews, PAA answers need to be direct.
If you add an H2 for "How long does an SEO audit take?", don't start with "It depends on many factors..."
Start with a direct answer like: "An SEO audit can take anywhere from 30 minutes to 6 weeks." Then you can explain the factors.
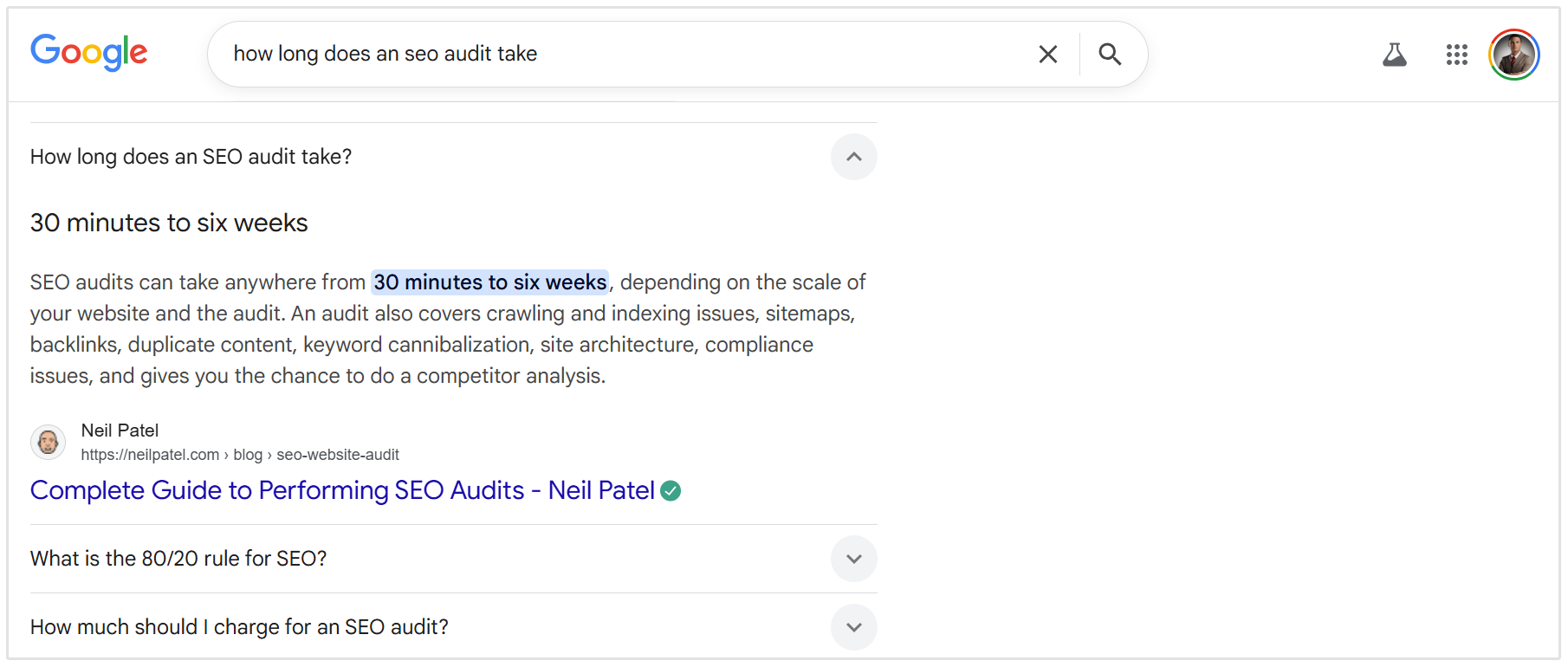
This micro answer approach signals to Google that you have a specific, extractable answer for that PAA slot.
How to Optimize for Local Pack
For local businesses, the Local Pack is non-negotiable. It relies on a different set of ranking factors than standard organic SEO.
Create and Optimize GBP
Your Google Business Profile (GBP) is the foundation of optimizing for local SEO.
Isaac Justesen, Founder & CEO at PatientPartners, says that having an optimized GBP is likely the most important thing local businesses can do to improve their SERP feature visibility.
A big part of getting into the local pack is having an optimized Google Business Profile. This means having a complete and current listing, using relevant categories, posting regularly, and generating lots of positive reviews.
Here are some tips for optimizing your GBP:
- Claim and Verify: Ensure you own the listing.
- Complete Every Field: Fill out services, hours, website, and appointment links.
- Select Categories Carefully: Your primary category has the biggest impact on ranking. Be specific (e.g., "Personal Injury Attorney" rather than just "Lawyer").
- Add Photos: regularly upload high-quality photos of your team, office, and work.
Ensure NAP Consistency
NAP stands for Name, Address, and Phone number. Google validates your business legitimacy by checking if your data is consistent across the web.
Ensure your NAP is exactly the same on:
- Your website (footer and contact page).
- Your Google Business Profile.
- Social media profiles (Facebook, LinkedIn).
- Local directories (Yelp, YellowPages, BBB).
Inconsistencies (like "St." vs "Street" or different phone numbers) can confuse Google and hurt your local rankings.
Related Reading: Local SEO: What Is It? And How Do You Improve?
How to Get into Image Pack and Video Carousel
Visual search is becoming increasingly important, especially for retail, DIY, and lifestyle topics.
Take for example if you search for any "how to..." phrase in Google, you'll likely get a video on the topic:
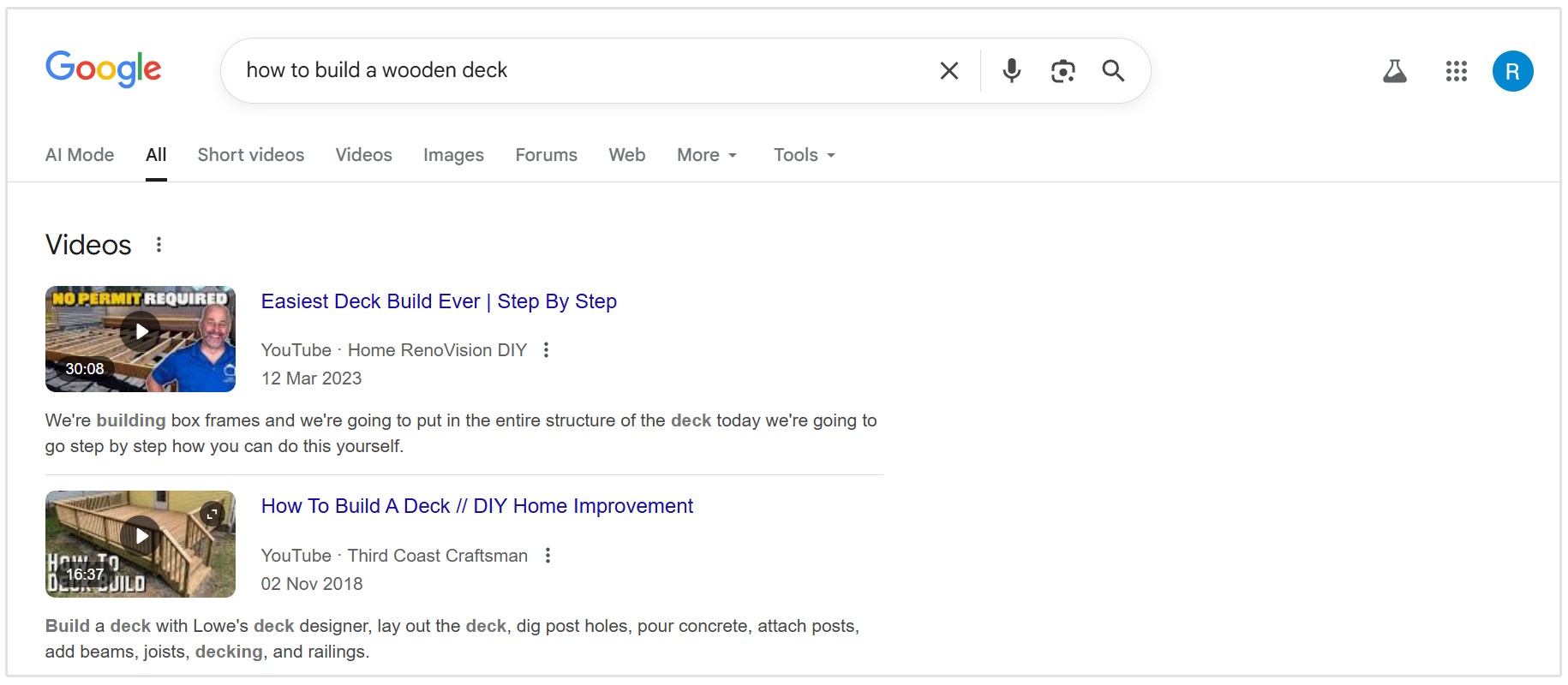
Video SEO Basics
Google loves YouTube. Follow these tips to rank in video carousels or video results in traditional search results:
- Use Chapters: In your YouTube video description, add timestamps (e.g., "02:15 - How to fix the leak"). Google uses these to create "Key Moments" in search results.
- Optimize Titles and Descriptions: Treat YouTube like a search engine. Use your target keywords in the video title and the first sentence of the description.
- Embed Video on Your Site: Embed the relevant video into your blog post. This helps Google associate the video with your written content.
Image Pack Optimization Basics
To appear in image packs:
- Alt Text: Always describe your image using alt text. Be descriptive and include the keyword naturally.
- File Names: Don't upload IMG_1234.jpg. Rename it to blue-running-shoes.jpg.
- Context: Place the image near relevant text. Google uses the surrounding text to understand what the image is about.
- Quality and Size: Use high-quality images, but compress them so they load fast. Google hates slow pages.
How to Get into Knowledge Panel
Getting a Knowledge Panel is tougher because you can't just "optimize" a page for it. You have to prove you are a notable entity.
Here are some top tips for getting into the Knowledge Panel:
- Wikipedia: A Wikipedia page is the surest way to get a Knowledge Panel, but it is difficult to obtain.
- Schema Markup: Use Organization or Person schema on your website's "About" page. This helps Google's bot connect the dots about who you are.
- Third-Party Validation: Google looks for consistent information about you across reputable third-party sites like Crunchbase, LinkedIn, and major news publications.
- Google Business Profile: For local businesses, your GBP often acts as your Knowledge Panel on branded searches.
Related Reading: How to Optimize for Google's Knowledge Graph in 5 Steps
Common Reasons You're Not Getting Into SERP Features
You have optimized your headers, written concise answers, and added schema... but still nothing. Here is why you might be missing out.
You’re answering the wrong intent
If the user wants a list (e.g., "top 10 horror movies") and you write a long essay, you won't win the snippet.
Check the current SERP. If Google shows a table, build a table. If Google shows a video, make a video. You must match the format the user wants.
Before writing anything, do the research and check what the search results are already showing. What you see displayed is what Google wants: boxes with short answers, questions, images, or lists. Your page should follow that same style, but better.
- Edmond Abramyan, Founder at Curious Fortune Media
Your answer is buried or too long
Google wants to give users a quick answer. If your definition of a term is 200 words long and starts with "In today's digital landscape...", it is too fluffy.
Give the direct answer first, then elaborate.
Wrong format for the feature Google is showing
Sometimes it comes down to code. If Google is displaying a "Recipe" rich snippet, it is almost entirely based on Schema markup.
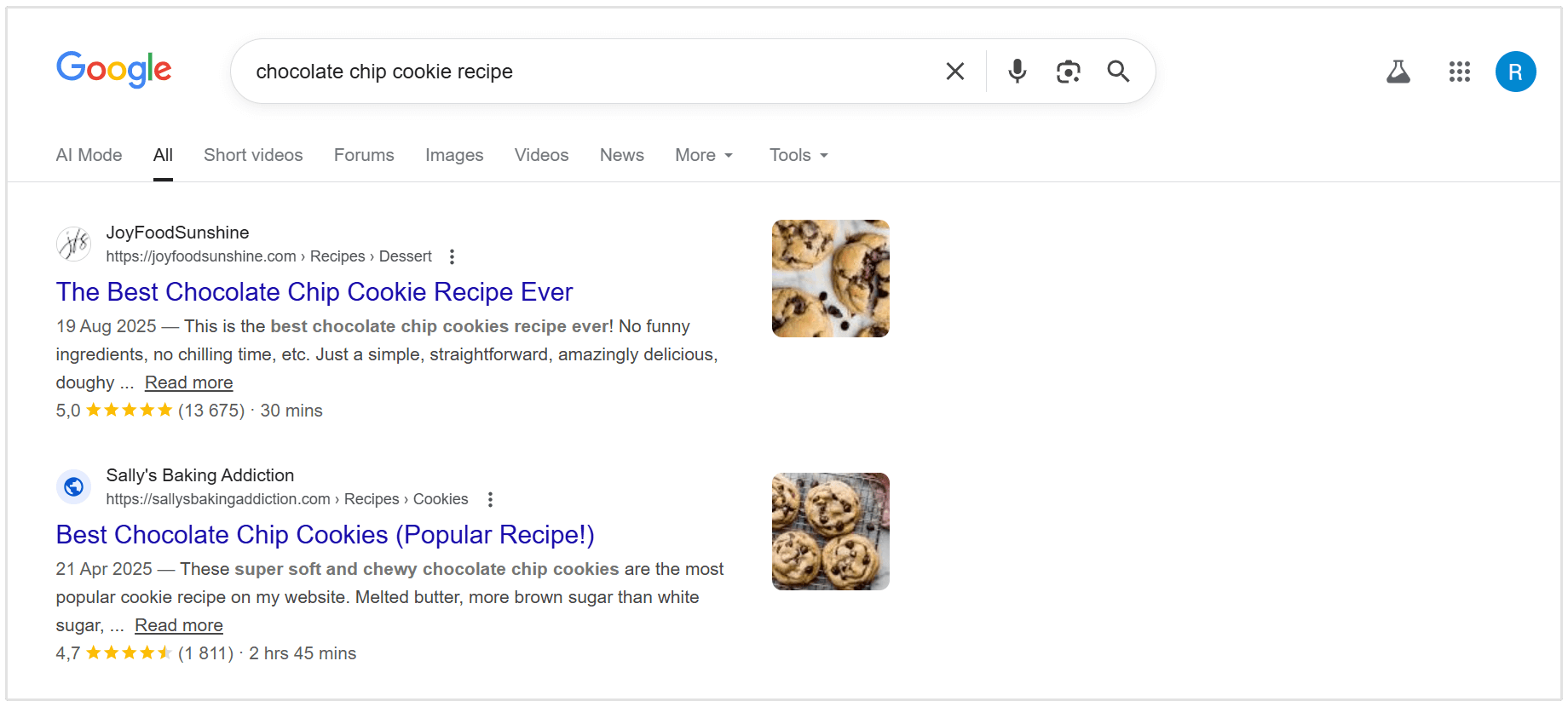
If you haven't implemented structured data (Schema) on your page, you are ineligible for these technical features.
Even when the content is strong, the lack of structured data alone can be the reason a page never becomes eligible for SERP features.
In our experience, the easiest way to get into various Google SERP features is to use structured data on your content. While not all SERP features are driven by this, we have many cases where schema updates made the difference.
- Andrew Shotland, Founder and CEO of Local SEO Guide
Conclusion
As Google moves toward zero-click searches and AI-generated answers, the traditional blue link is losing its dominance.
By structuring your content to answer questions directly, using the right HTML formatting, and leveraging Schema markup, you can increase the odds of getting into SERP features.
Start by:
- Auditing your top-ranking pages and content
- Looking for PAA opportunities in existing content
- Adding snippet-ready definitions
- Ensuriong your visual assets are optimized
- Creating and optimizing a GBP (if you haven't already)
The landscape of search is changing. Don't just aim to rank; aim to get into SERP features too.